Figure 4.
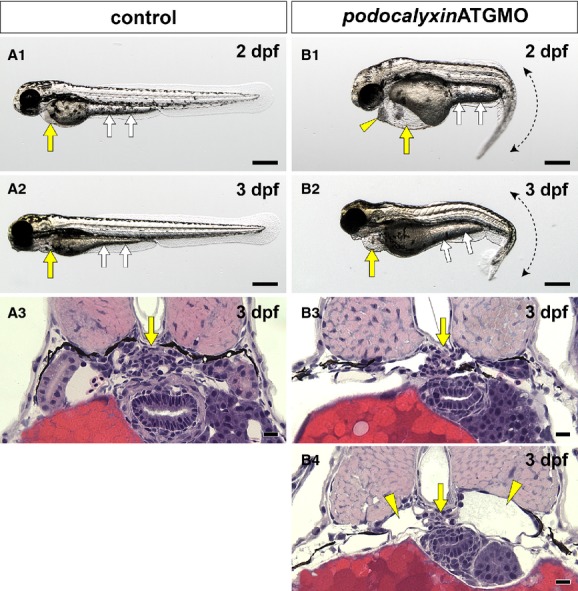
Translational blocking of podocalyxin caused pronephric glomerular hypoplasia. (A1, A2 and B1, B2) Whole-body images. Pericardial sac (yellow arrows) and yolk sac extension (white arrows) are larger in the podxlATGMO morphants on 2 and 3 dpf (B1, B2) than in the uninjected control larvae (A1, A2). This enlargement resulted from edema. The podxlATGMO morphants also have tail curvatures (B1, B2). In the 2-dpf morphants, cellular aggregation is consistently found at the anterior pole of pericardial sac (arrowhead in B1). (A3 and B3, B4) Hematoxylin–eosin staining sections showing pronephric glomerulus. In 3-dpf control larvae, a pair of pronephric nephron primordia merges to form a single glomerulus (arrow in A3). In the podxlATGMO morphants, their pronephric glomeruli exhibit hypoplasia (arrows in B3, B4). Some of the morphants display bilateral cystic dilatation of Bowman's capsule and pronephric tubule (arrowheads in B4). Bar scales, 250 μm in A1, A2, B1, B2; 10 μm in A3, B3, B4.
