Figure 2.
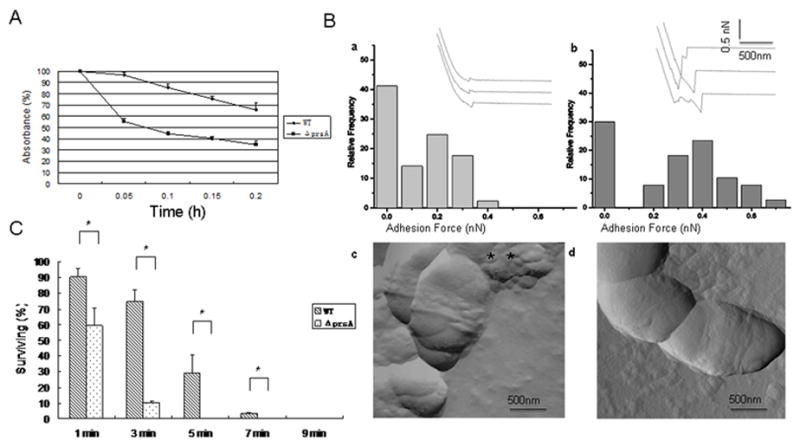
Cell surface characteristics. (A) Hydrophobicity: Adherence of S. mutans UA140 wild type and its prsA-deficient derivative to hexadecane in the BATH assay. Results are expressed as percentage absorbance of the aqueous phase after hexadecane treatment relative to the initial absorbance. Each point represents the mean of three independent experiments. (B) AFM analysis: Adhesion histograms and representative force curves (inset) recorded with hydrophobically modified tips on S. mutans UA140 (a) and the prsA-deficient strain (b) using a maximum applied force of 1nN. The surface topographies of wild type (c) and mutant strain (d) were also observed (amplitude images) using high-resolution AFM imaging. Two biological replicates were performed and representative image are shown. (C) Resistance of S. mutans UA140 and the prsA-deficient strain to sonication at a constant frequency of 22 kHz. Results are expressed as percentage of viable cells after sonication relative to untreated cells. Each point represents the mean ± SD of two independent measurements. The asterisk indicates that prsA-deficient strains were significantly less resistant to sonication than wild type at the same treatment time point (Student’s t test p value <0.05).
