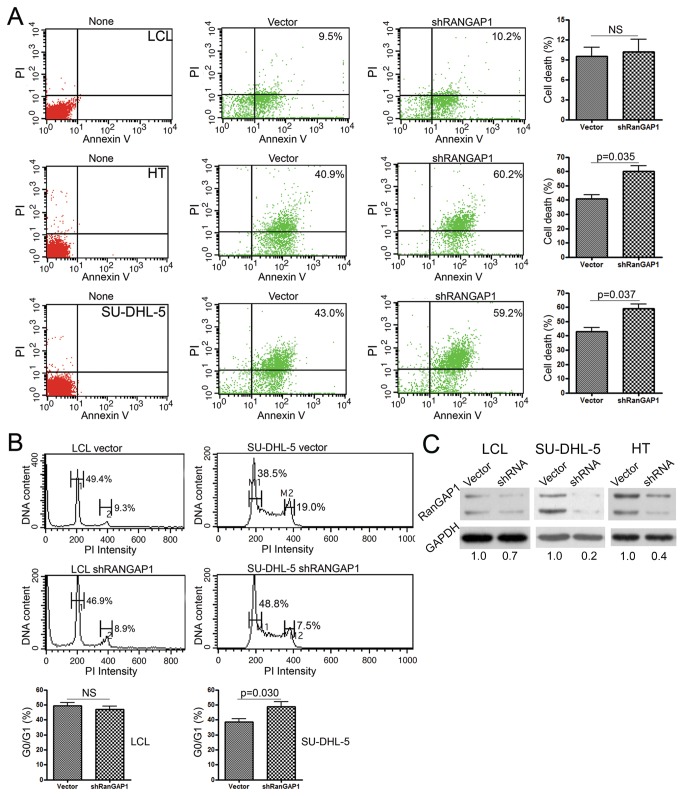
Figure 3. RanGAP1 RNA interference increased tumor cell death and cell-cycle arrest but had no effect on non-neoplastic LCL cells.
(A) After transfection, the effect of inhibiting RanGAP1 was evaluated in the LCL (upper panel), HT (middle panel), and SU-DHL-5 cell lines (lower panel) for cell death, measured using annexin V and PI (propidium iodide). LCL cells show no difference in cell apoptosis between control vector (9.5%) and shRANGAP1 (RANGAP1-specific shRNA) (10.2%; NS, not significant). In contrast, apoptosis was higher in the HT (vector, 40.9% vs. shRANGAP1, 60.2%, p = 0.035) and SU-DHL-5 cell lines (vector, 43.0% vs. shRANGAP1, 59.2%, p = 0.037). None: non-transfected maternal cells. (B) Cell-cycle analysis shows no effect on LCL (left panel, 1: G0/G1, vector, 49.4% vs. shRANGAP1, 46.9%; 2: G2/M, vector, 9.3% vs. shRANGAP1, 8.9%; NS, not significant), but it does show G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest in SU-DHL-5 cells (right panel, M1: G0/G1, vector, 38.5% vs. shRANGAP1, 48.8%; M2: G2/M, vector, 19.0% vs. shRANGAP1, 7.5%, p = 0.030). (C) Western blotting shows a marked decrease (vector, 1.0 vs. shRANGAP1, 0.2 with GAPDH normalization) of RanGAP1 expression in SU-DHL-5 and HT (vector, 1.0 vs. shRANGAP1, 0.4) after RNA interference of RANGAP1 by shRNA.