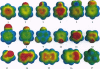
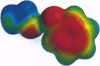
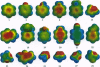
Abstract
The cation-pi interaction is an important, general force for molecular recognition in biological receptors. Through the sidechains of aromatic amino acids, novel binding sites for cationic ligands such as acetylcholine can be constructed. We report here a number of calculations on prototypical cation-pi systems, emphasizing structures of relevance to biological receptors and prototypical heterocycles of the type often of importance in medicinal chemistry. Trends in the data can be rationalized using a relatively simple model that emphasizes the electrostatic component of the cation-pi interaction. In particular, plots of the electrostatic potential surfaces of the relevant aromatics provide useful guidelines for predicting cation-pi interactions in new systems.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dougherty D. A. Cation-pi interactions in chemistry and biology: a new view of benzene, Phe, Tyr, and Trp. Science. 1996 Jan 12;271(5246):163–168. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5246.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty D. A., Stauffer D. A. Acetylcholine binding by a synthetic receptor: implications for biological recognition. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1558–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.2274786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpf R. A., Dougherty D. A. A mechanism for ion selectivity in potassium channels: computational studies of cation-pi interactions. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1708–1710. doi: 10.1126/science.8378771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Z., Johnson M. E. Proposed cation-pi mediated binding by factor Xa: a novel enzymatic mechanism for molecular recognition. FEBS Lett. 1995 Aug 14;370(1-2):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00811-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]