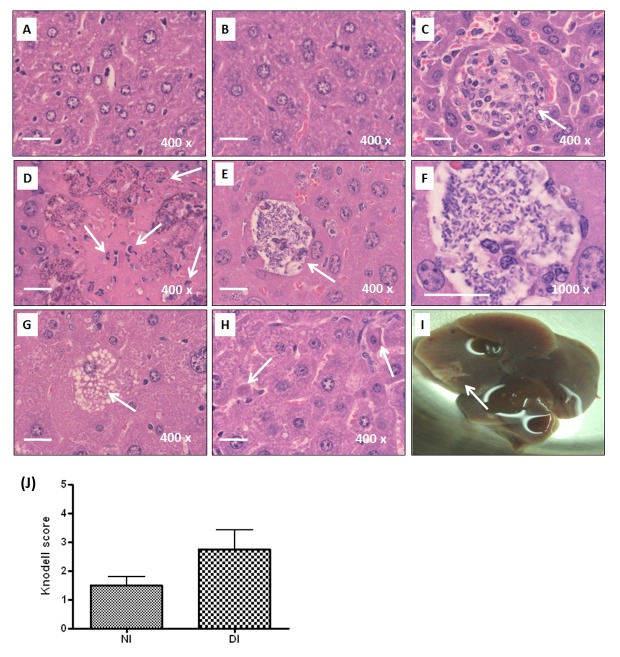
Figure 3. Histopathological examination of liver.
For all the experimental groups, liver sections were prepared from the liver retrieved at 72 hpi, stained with H/E, and imaged under microscopic observation with magnification of 400×. Representative liver sections of PBS-control naïve mice (A), PBS-control diabetic mice (B), and the K. pneumoniae-infected naïve mice (C) are shown. Infiltrates of neutrophils and lymphocytes are indicated with arrows. Several characteristics revealed on the liver section from the K. pneumoniae-infected diabetic mice, including liquefactive necrosis with degeneration of liver parenchyma and inflammatory cells (D), accumulation of K. pneumoniae (E and F), ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes (G), and the formation of Councilman body (H) are shown with an indication of arrows. A large hepatic abscess was noted in the right liver lobe of a K. pneumoniae-infected diabetic mouse (I). Scale bar represents a distance of 20 μm. (J) Hepatic injury graded by the Knodell necroinflammatory scoring system. Livers were retrieved from K. pneumoniae-infected naïve mice (NI; n=4) and diabetic mice (DI; n=8). Statistical analysis by the Mann-Whitney U test (one-tailed) showed no significant difference between NI and DI groups.