Figure 5. Activation of IFN-γ/STAT/IRF-1 signaling in hepatic responses to K. pneumoniae infection.
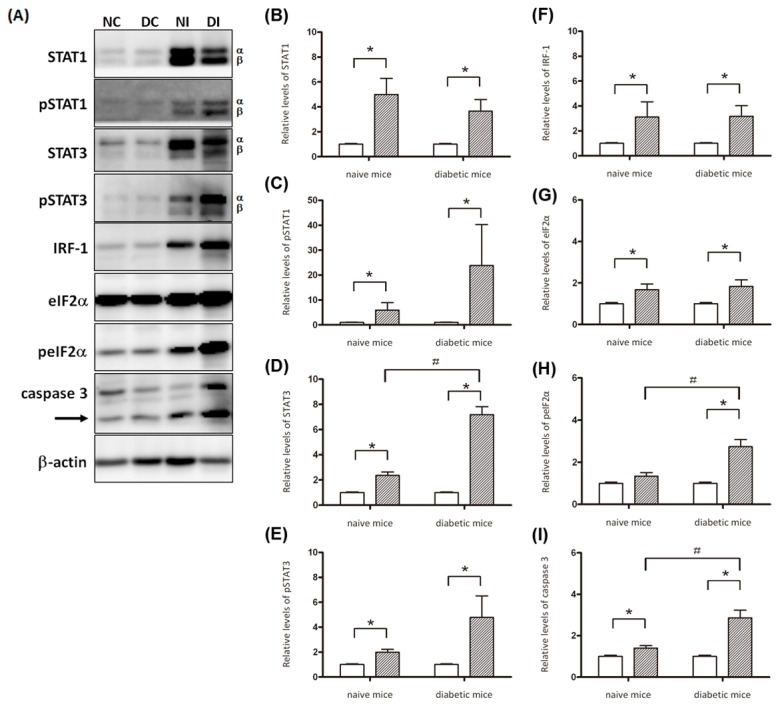
Liver lysates were prepared from PBS-control naïve mice (n=3), PBS-control diabetic mice (n=3), and the K. pneumoniae-inoculated naive and diabetic mice which had developed an extraintestinal infection at 72 hpi (the sample size in naïve and diabetic groups is 4 and 8, respectively). Thirty micrograms of total proteins were subjected to Western blot analyses with specific antibodies. Western blotting analysis was repeated for three times by independent experiments. A representative result is shown in (A). Band intensity for each protein was determined by Densitometry calculation and normalized with β-actin. Data from three independent experiments for the expression level of (B) STAT1, (C) phospho-STAT1, (D) STAT3, (E) phospho-STAT3, (F) IRF-1, (G) eIF2α, (H) phospho-eIF2α, and (I) activated caspase 3 are shown as means ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by the Mann-Whitney U test (one-tailed). *P < 0.05 (one-tailed) represents a significant increase in the K. pneumoniae-infected naïve or diabetic group (slash bar) in comparison with the corresponding control group (empty bar). # P < 0.05 (one-tailed) for significant difference between the naïve and diabetic mice which were K. pneumoniae-infected.
