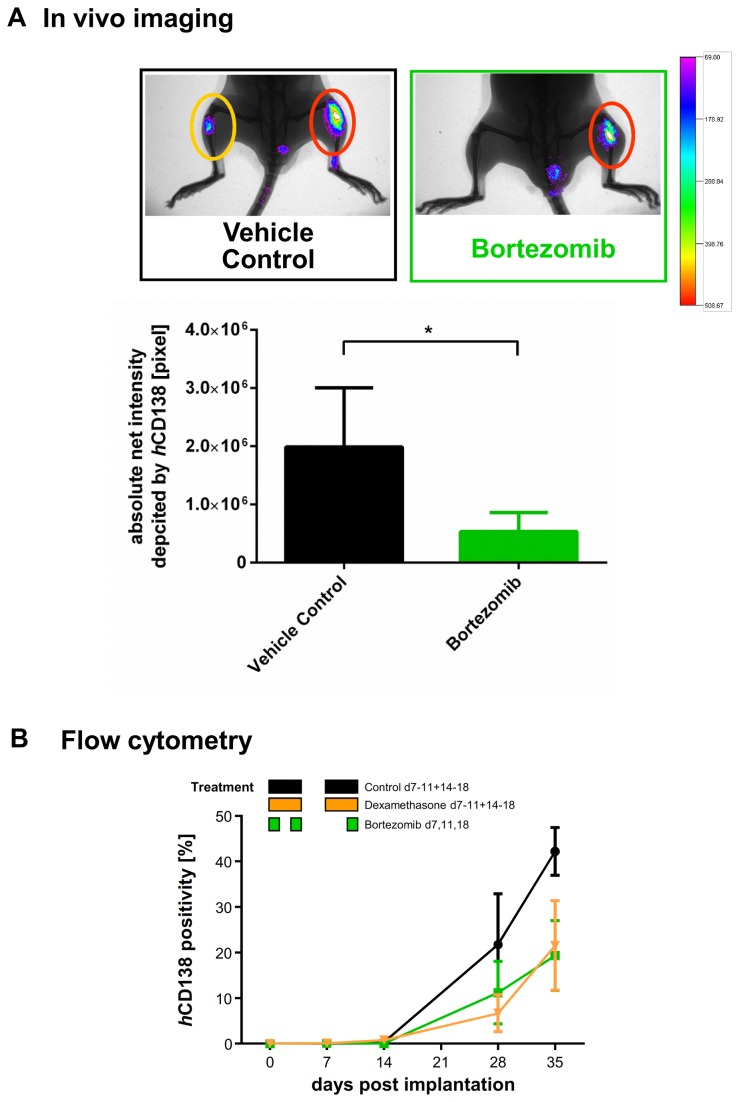
Figure 5. A. Chemosensitivity of L363 cells in NSG against different antimyeloma agents determined by flow cytometry.
A total of 24 NSG received it-injections of 2x105 L363 cells: seven days thereafter, 18 mice were randomized into three groups of six animals each. Six additional mice were analysed on the first treatment day (d7) to determine tumor load before the respective therapies. MM cell engraftment was determined by flow cytometry using hCD138-Ab (n = 2-3 per group and time point, 4 measurements per group over the time). Black: mice were treated with control vehicle (0.9% NaCl, i.p. d7-11, 14-18). Yellow: mice were treated with 3 mg/kg/d dexamethasone, i.p. (d7-11, 14-18). Green: mice were treated with 0.7 mg/kg/d bortezomib, iv (d7, 11, 18). 7, 14, 28 and 35 days after implantation, tumor cells were assessed via flow cytometry and increased detectably. Analyses on day 35 confirmed that tumor growth was reduced with dexamethasone by 51% and with bortezomib by 66%. B. Chemosensitivity of L363 cells in NSG against different antimyeloma agents determined by fluorescence-based-IVI. A total of 15 NSG received it-injections of 2x105 L363 cells: seven days thereafter, mice were randomized into two groups of six and nine animals, respectively. IVI using Alexa750 tagged hCD138 antibody was employed to determine tumor engraftment and treatment efficacy. In addition animals were x-rayed and the two pictures merged for optimal localization of the fluorescent region. Tumor growth after bortezomib treatment on day 18 was significantly reduced which was observed both for primary and metastatic sites (Student`s t-test, one-tailed p< 0.05). Error bars depict standard deviation.