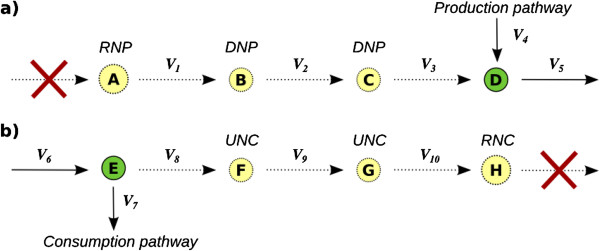
Figure 1.
Description of gap metabolites. A schematic representation where the four classes of gap metabolites are shown as a consequence of missing reactions. Red crosses indicate the absence of some reaction. Dotted and continuous arrows represent blocked and non-blocked reactions, respectively. Yellow and green circles represent gap and non-gap metabolites, respectively. Metabolites are labeled according to its class. In a) the absence of a reaction, causes metabolite A to become a Root-Non-Produced metabolite (RNP) and this effect propagates downstream generating new gap metabolites (Downstream-Non-Produced, DNP) and blocked reactions. In b) the absence of reactions consuming H makes it a Root-Non-consumed metabolite (RNC) and this effect propagates upstream causing other metabolites to become Upstream-Non-Consumed (UNC), in a symmetric manner respect to case a).