Fig. 5. Effect of pH 5.0 on the overall structure of CRP.
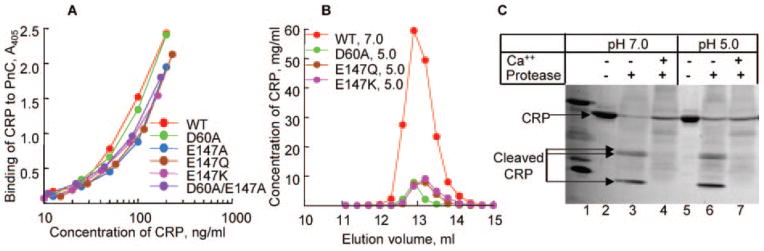
A, binding of purified WT and mutant CRP, dialyzed against TBS, pH 5.0, to PnC. Microtiter wells were coated with PnC. Increasing concentrations of various CRP species in a TBS-Ca were added to the wells. Bound CRP was detected by HD2.4 mAb. A representative of two experiments is shown. B, elution profiles of purified nCRP at pH 7.0 and purified mutant CRP dialyzed against TBS, pH 5.0, from the Superose12 gel filtration column. C, Ca2+ site-dependent proteolytic cleavage of CRP. Purified nCRP at pH 7.0 and 5.0 was subjected to proteolytic cleavage in the absence and presence of Ca2+. A representative of 2–3 experiments is shown.
