Figure 1.
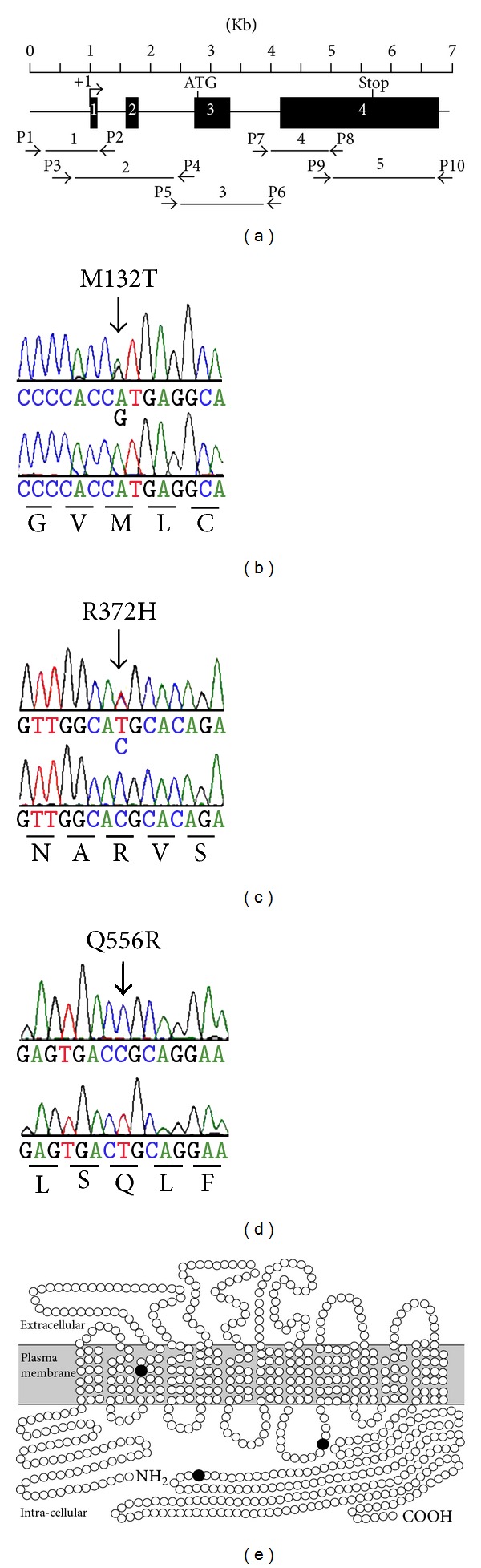
Identification of variants in the human SLC26A1 gene and predicted amino acid substitutions. (a) Schematic of SLC26A1 showing 4 exons (boxes), transcription initiation site (+1, arrow), and the relative location of PCR primers (P1–P10) and PCR amplicon fragments (1–5) used for DNA sequence analysis. ((b)–(d)) Representative DNA sequence chromatographs showing variant (top panels) and control (bottom panels) sequences that predict (b) heterozygous M132T, (c) heterozygous R372H, and (d) homozygous Q556R. Reverse complement nucleotide sequences are shown. (e) Position of amino acid substitutions (•) in the predicted secondary structure model of the human SAT1 protein [25]. M132T within the third transmembrane domain; R372H in the fourth intracellular loop; and Q556R in the intracellular carboxy-terminal domain.
