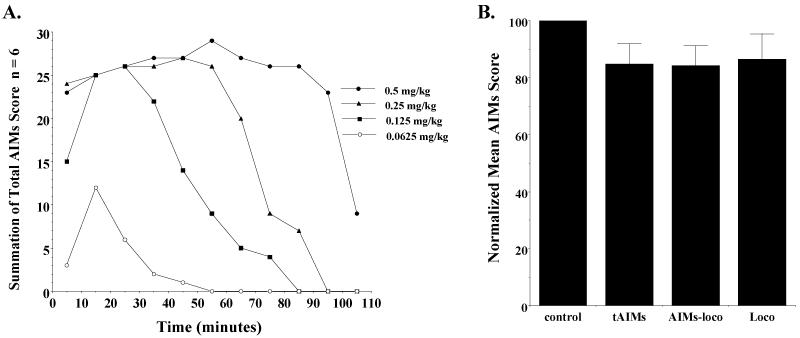
Figure 11. SKF 81297 dependent induction of abnormal involuntary movements and the effect of PG01037 on SKF 81297 dependent abnormal involuntary movements in unilaterally lesioned animals.
(A) The temporal plots for the induction of abnormal involuntary movements in unilaterally lesioned rats is shown. Summation of total AIM scores (n = 6) were determined at 10 minute intervals starting at t = 5 minutes. SKF 81297 was administered s.c. at the following doses: a) 0.5 mg/kg (●), b) 0.25 mg/kg (▲), c) 0.125 mg/kg (■) and d) 0.0625 mg/kg (○). (B) The effect of PG01037 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) on SKF 81297 (0.1 mg/kg, s.c.) on the total AIMs (tAIMs), AIMs minus locomotor activity (AIMs-loco) and locomotor activity (Loco) scores is shown. PG01037 or vehicle was administered 10 minutes prior to the administration of SKF 81297. The data are the normalized mean values ± S.E.M. for n = 9 animals. The normalized mean scores for each is as follows: a) total AIMs, 84.7 ± 7.3; b) AIMs-locomotor, 84.2 ± 7.0; c) locomotor score, 86.4 ± 9.0. The significance level for each of these scores compared to the vehicle control (control) is p ≥ 0.09.