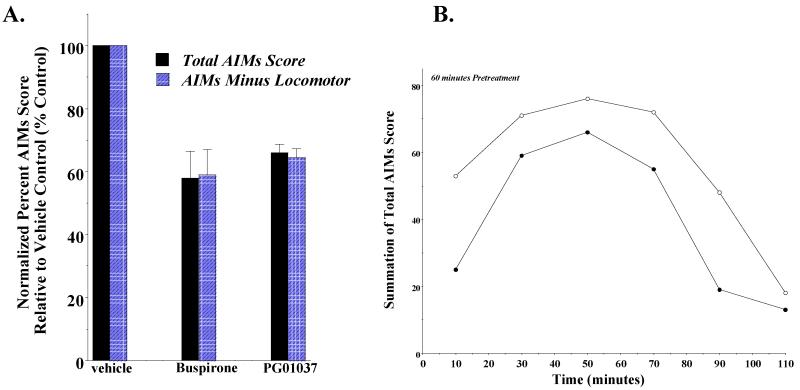
Figure 4. Effect of administration of PG01037 or buspirone 60 minutes prior to L-dopa administration on rat AIMs score.
(A) A comparison was made of the ability of PG01037 (10 mg/kg; n = 9) and buspirone (4 mg/kg; n = 11) to attenuate L-dopa-dependent AIMs in rats. Both drugs were administered i.p. 60 minutes prior to the L-dopa (8 mg/kg). This graph shows the mean total AIM scores (solid bars) ± S.E.M. and the total AIMs score minus the locomotor component (hatched bars) ± S.E.M. for PG01037 (65.9 ± 2.7 and 64.7 ± 2.9) and buspirone (57.9 ± 8.5 and 58.9 ± 8.1), respectively. Under these conditions both drugs statistically decreased the abnormal involuntary movements (p < 0.0001). (B) The variation in the total AIMs minus the locomotor component score as a function of time is shown using a 60 minute pretreatment time with 10 mg/kg PG01037 (●) or vehicle control (○). Each point is the summation of total AIMs minus the locomotor scores for 11 animals at each observation time point. This represents a mean 34.1 ± 8.0 (S.E.M.) percent reduction in the AIMs minus locomotor score over the observation time. Plots of the summation of the total AIMs score are essentially identical in shape with a 35.5 ± 8.4 percent reduction in the mean score.