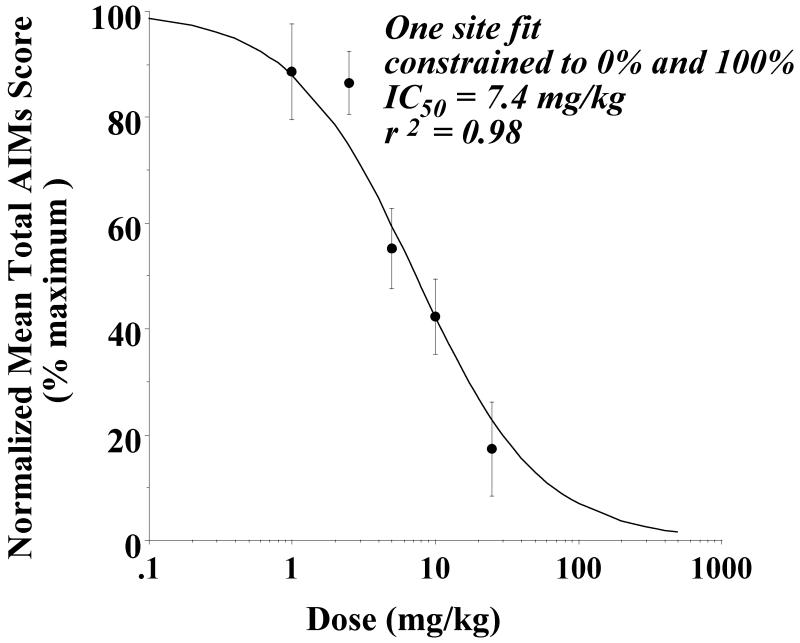
Figure 6. Concentration dependence analysis to determine the effect of doses of PG01037 on AIM scores.
Unilaterally lesioned rats were injected (i.p.) with varying doses of PG01037 (0 to 25 mg/kg) followed immediately with a constant dose of L-dopa and benserazide (8 mg/kg each). The percent of the mean total AIMs score ± S.E.M. (n ≥ 8) relative to vehicle controls as a function of the dose of PG01037 is shown. The mean values ± S.E.M. for the normalized total AIMs values as a function of PG01037 concentrations are as follows: a) 1 mg/kg, 88.6 ± 9.1, b) 2.5 mg/kg, 86.6 ± 5.9, c) 5 mg/kg, 55.2 ± 7.6, d) 10 mg/kg, 42.4 ± 7.1 and e) 25 mg/kg, 17.3 ± 8.9. A graph of the percent change in the AIMs score minus the locomotor component as a function of the dose of PG01037 is essentially identical to the one shown in this figure. At doses of 1 and 2.5 mg/kg there is not a significant attenuation of the total AIMs score. However, at doses of 5, 10 and 25 mg/kg there was a significant reduction (p < 0.0001) of total AIM scores relative to the vehicle controls. The calculated IC50 value was found to be 7.4 mg/kg using a reversible one site fit model constraining the maximum and minimum mean values to 100% (no test drug) and 0%, respectively.