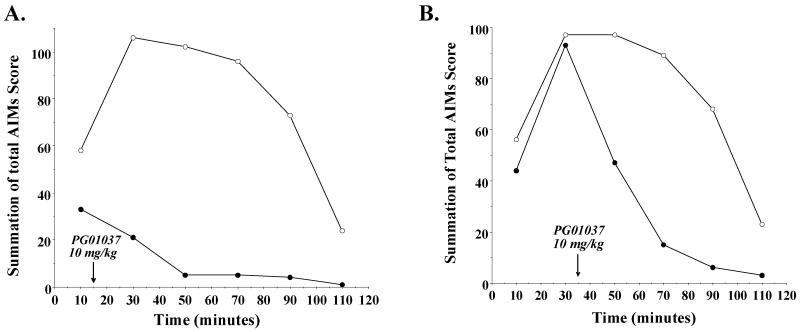
Figure 7. Effect of post treatment of PG01037 on the temporal expression of L-dopa dependent AIMs in lesioned rats.
(A) The variation in the total AIMs score as a function of time is shown using 10 mg/kg PG01037 (●) or vehicle control (○) fifteen minutes after L-dopa/benserazide (8 mg/kg each) administration. Each point is the summation of total AIM scores for 11 animals at each observation time point. This represents a mean 86.5 ± 3.9 (S.E.M.) percent reduction in the total AIMs score over the total observation time. The time (minutes) denotes that amount of time following the administration of the L-dopa/benserazide and the arrow marks the time of the administration of PG01037. Plots of the summation of the AIMs score minus the locomotor component are essentially identical in shape. (B) The variation in the total AIMs score as a function of time is shown using 10 mg/kg PG01037 (●) or vehicle control (○) thirty five minutes after L-dopa/benserazide (8 mg/kg each) administration. Each point is the summation of total AIM scores for 11 animals at each observation time point. This represents a mean 47.6 ± 8.2 (S.E.M.) percent reduction in the total AIMs score over the total observation time. The time (minutes) denotes the amount of time following the administration of the L-dopa/benserazide and the arrow marks that time of the administration of PG01037. Plots of the summation of the AIMs score minus the locomotor component are essentially identical in shape.