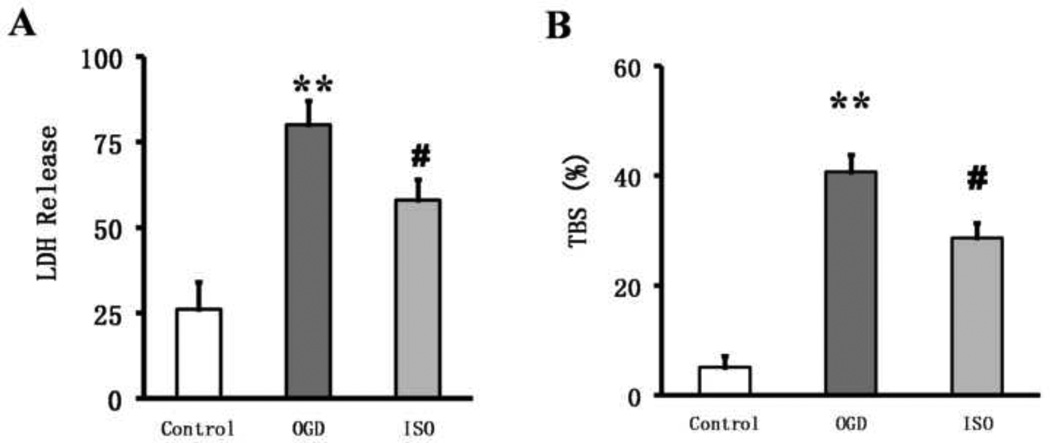
Figure 1.
Isoflurane post-conditioning increases neuronal viability after oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) injury. (A) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity expressed as a percentage of total LDH (determined for each experiment by assaying the supernatant of sister cultures after 30 min of exposure to 1% Triton X-100) indicates that OGD increases cell death. Isoflurane (ISO) partially restored viability. The data were obtained from three independent experiments with at least eight wells per condition. (B)Trypan blue staining (TBS) showed that the viability of primary cultured cortical neurons was decreased with OGD exposure but partially restored by isoflurane post-conditioning. Data are presented as mean±SD (n=9/group). **P<0.01 vs. the control group. #P<0.05 vs. the OGD group.