Figure 1.
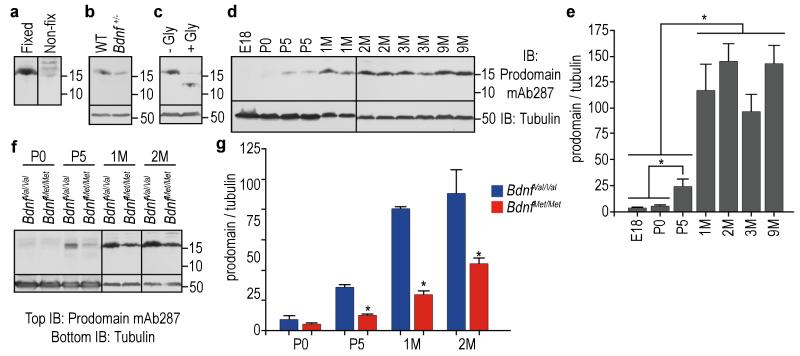
The BDNF prodomain is detected at high levels in vivo. (a) Detection of BDNF prodomain (15.5 kDa.) from mice hippocampus after glutaraldehyde fixation of the transfer membrane following SDS-PAGE. (b) The prodomain levels were reduced by half in Bdnf+/− mice hippocampal lysates, compared to wild type animals (WT). (c) Treatment of hippocampal lysates with N-glycanase (+Gly) reduced the molecular weight of the prodomain to 12.3 kDa. (d) BDNF prodomain levels at embryonic day 18 (E18), postnatal days 0 and 5 (P0 and P5), and 1, 2, 3 or 9 months (M) in hippocampal lystes of C57BL/6 mice. (e) Quantification of (d). Bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of prodomain densitometry data normalized to β tubulin. n=3 per group. (f) Comparison of BDNF prodomain levels from hippocampi of BdnfVal/Val and BdnfMet/Met mice at P0, P5, 1 and 2 month of age. (g) Quantification of (f). Bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of prodomain densitometry data normalized to β tubulin. n=4 per group. Statistical comparisons were made by one way analysis of variance test. * p < 0.05.