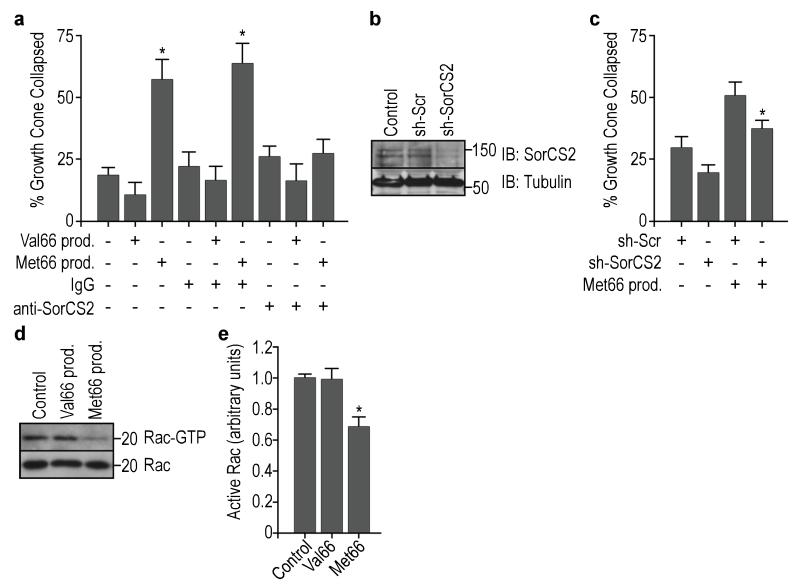
Figure 7.
Met66-SorCS2 interaction is required to induce growth cone retraction. (a) SorCS2 antibodies were able to block the Met66 prodomain-induced growth cone retraction. Neurons were pre-incubated with anti-SorCS2 (or control IgGs), treated with Val66 or Met66 prodomains (10 ng/ml) for 20 min, and followed by growth cone retraction analysis. Quantification assessed in p75NTR positive cells from 3 independent experiments. (b) Representative blot showing SorCS2 expression in cultured hippocampal neurons after knock-down using SorCS2 shRNA (sh-SorCS2) lentivirus infection, as compared to uninfected controls or scramble shRNA (sh-Scr) infected cells. (c) SorCS2 partial down regulation achieved with SorCS2 shRNA was able to partially prevent the Met66 prodomain-induced growth cone retraction. Quantification of 4 independent experiments. (d) Only Met66 prodomain administration, but not the Val66, induced a decrease in Rac activity in cultured hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal neurons were incubated with Val66 or Met66 prodomain for 20 min, and cell lysates were incubated with GST-PAK-CRIB beads to isolate activated Rac (Rac-GTP). (e) Quantification of (d). Activated Rac was measured by densitometry and normalized to total Rac in the input. Quantification assessed in 4 independent experiments. Bars represent mean ± s.e.m. Statistical comparisons were made by one way analysis of variance test. * p <0.05.