Fig. 3.
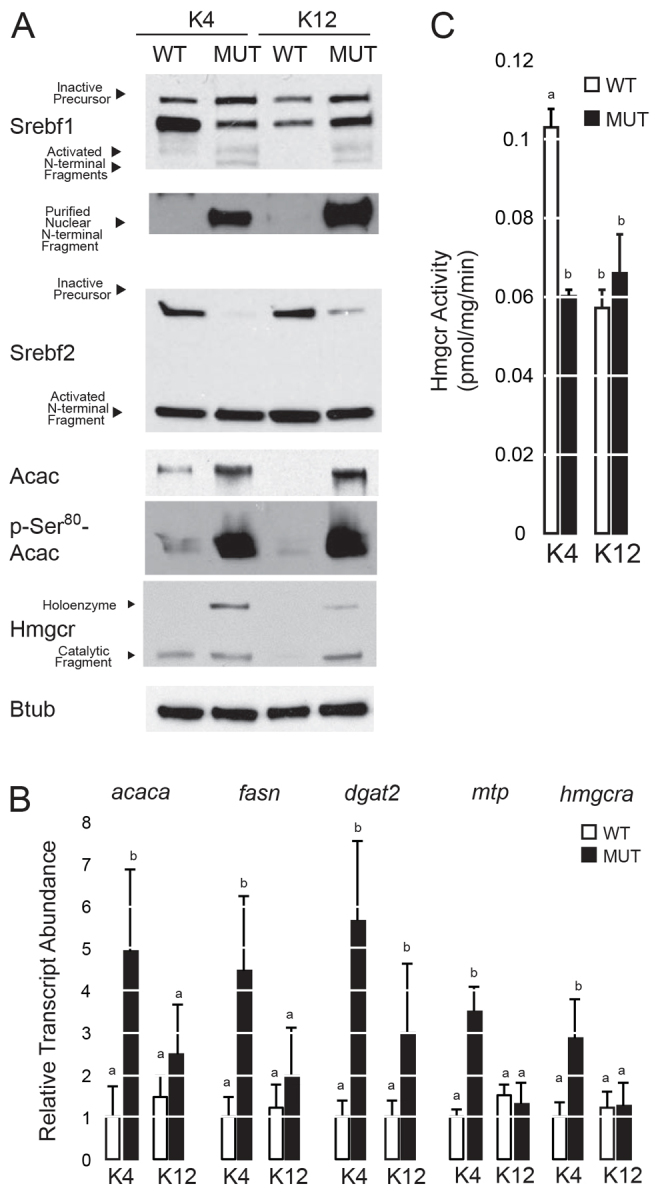
Activation of Srebf pathways in slc16a6a mutant livers. After 45 days of feeding wild-type (WT) and mutant (MUT) animals ketogenic diets (K4 or K12), livers were harvested and analyzed. (A) Immunoblot analysis of Srebf1, Srebf2, Acac, phospho-Ser80 Acac, Hmgcr and Btub (β-tubulin) (five livers pooled per lane). For Srebf1, an additional nuclear isolation is shown (bottom) because maturation of this transcription factor is not as striking in whole lysates as it is for Srebf2. (B) Abundance of select transcripts encoding enzymes of de novo lipogenesis and cholesterol biosynthesis measured by quantitative PCR (n=5). Groups with different letters are statistically different, P<0.05. Tukey’s HSD. All data are mean ± s.e.m. (C) Hmgcr activity in liver homogenates (n=4). Groups with different letters are statistically different, P≤0.001. Tukey’s HSD. All data are mean ± s.d.
