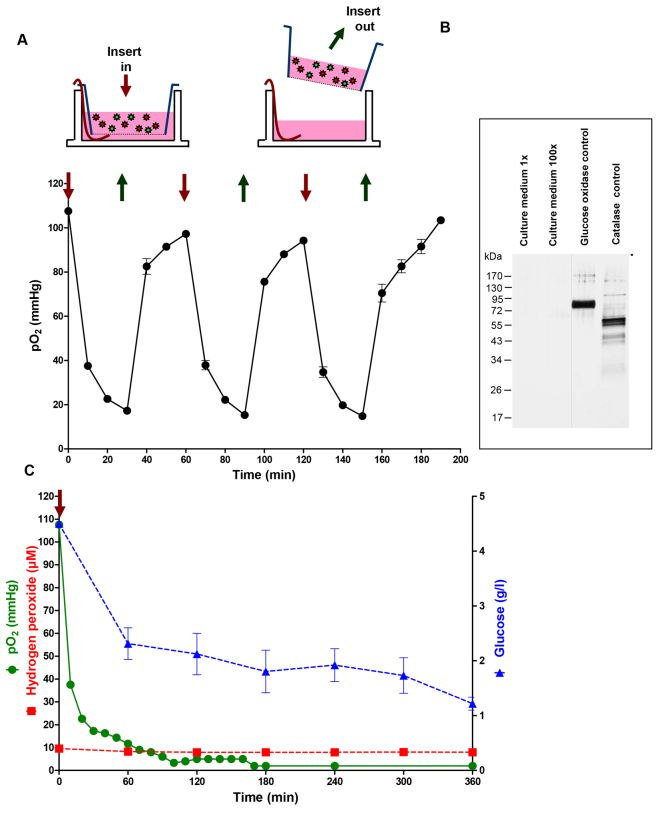
Fig. 2.
Characterization of transient and long-term hypoxic conditions induced by the insert-based two-enzyme system. (A) Application of the enzyme-containing insert (red arrow) results in a rapid decrease in pO2. After removing the insert (dark green arrow), pO2 quickly increases to almost baseline levels. This on-off procedure can be repeated, yielding similar pO2 profiles each time. (B) Silver staining experiments show that the hypoxia-inducing enzymes are restrained within the insert and do not pass the semipermeable membrane. (C) Applying the enzyme-containing insert for a prolonged time period results in a decrease of pO2 to values as low as 2.00 mmHg. Hypoxic conditions are stable for at least 6 hours. During the experiment, glucose concentrations gradually decrease, whereas hydrogen peroxide levels keep at a steady state. Bars denote mean ± s.e.m. of three experiments.