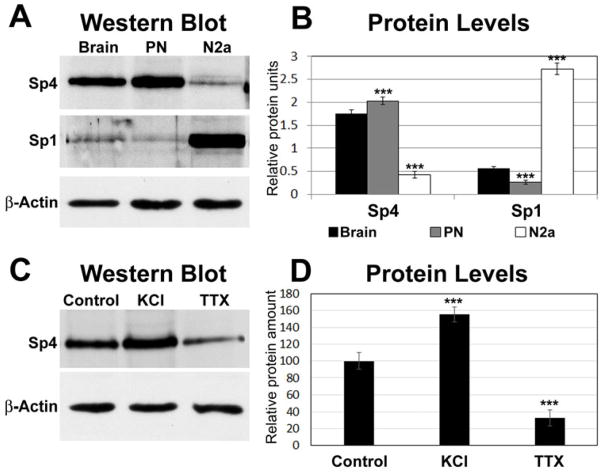
Fig. 4.
Over-expression of Sp4 in N2a cells (A – C) or in primary neurons (D) increased expression of all thirteen COX subunits. A, Up-regulation of Sp4, COX1, and COX4i1 protein levels in cells transfected with Sp4 expression vectors as compared to empty vector controls. Lane 1, empty vectors; Lane 2, Sp4 over-expression. N = 6 for each group. B, Quantification of protein levels shown in A. Solid bars, controls; open bars, Sp4 over-expression. C, Sp4 over-expression led to a significant up-regulation of Sp4, mitochondrial encoded COX subunits (COX1, COX2, and COX-3), mitochondrial transcription factors (TFAM, TFB1M, and TFB2M), SURF1, and nucleus-encoded COX subunits (COX4i1 - COX8a) as compared to empty vector controls. N = 6 for each group. All * P values were compared to empty vectors. ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001 when compared to empty vectors. D, Sp4 over-expression in primary neurons also led to a significant up-regulation of Sp4, mitochondrial encoded COX subunits (COX1, COX2, and COX-3), mitochondrial transcription factors (TFAM, TFB1M, and TFB2M), SURF1, and all 10 nucleus-encoded subunits (COX4i1 - COX8a) compared to empty vector controls. N = 3 for each group. All * P values were compared to empty vectors. ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001.