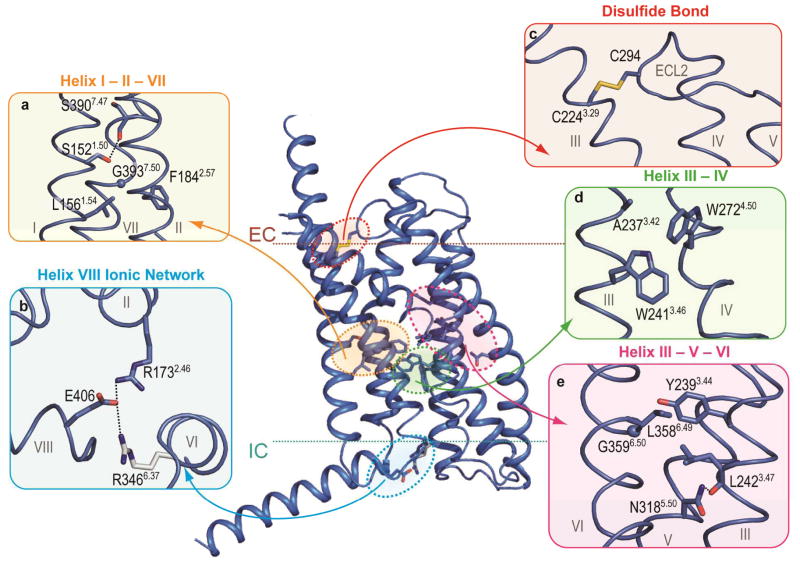
Figure 3. Structural features of class B GPCRs.
Comparison of GCGR and class A GPCRs crystal structures indicates distinct and conserved features. a, d, and e, The homologous GCGR residues involved in helix I – II, III – IV, and III –VI interface interactions as discussed for class A receptors by Venkatakrishnan et al25, and class B GPCR specific residues that mediate helix I – VII, II – VII, and III – V interface interactions. b, GCGR residues Glu406 of helix VIII, Arg1732.46, and Arg3466.37 form a class B receptor specific ionic network. Arg3466.37 (grey) has a weak electron density. c, The disulfide bond between Cys2243.29 and Cys294ECL2 in the GCGR structure, a conserved feature between classes A and B receptors. Hydrogen bond interactions are indicated by black dashed lines. Electron density maps for residues in this figure are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10.