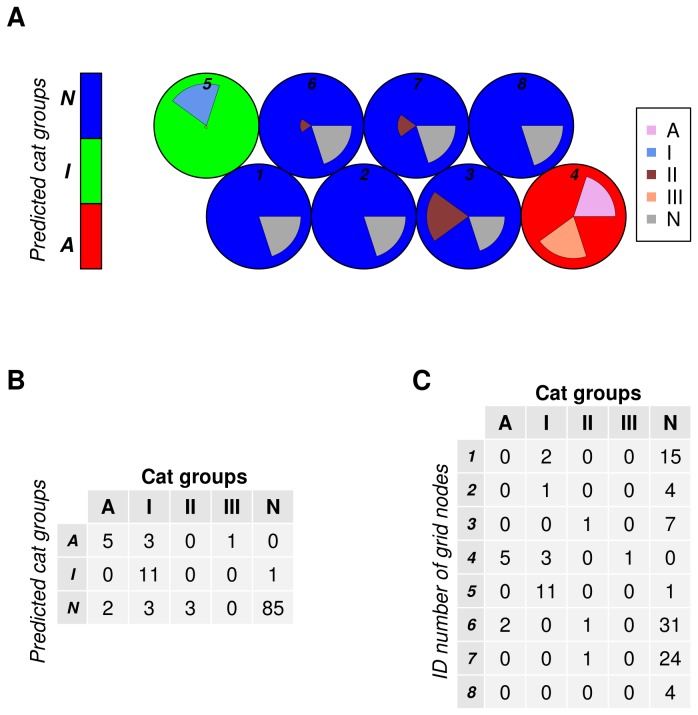
Figure 6. Naturally Toxoplasma gondii seropositive cats and cats with a known clonal type II infection recognized similar peptide patterns.
To explore whether there are particular patterns of anti-peptide reactions among all serologically positive T. gondii cat sera, a XY-fused Selforganizing Kohonen Network analysis (XYF-SKN) was performed. Figure (A) presents the clustering of various groups of T. gondii positive cat sera in a Y-map. Most of the sera derived from cats infected with non-canonical T. gondii types (A), infected by clonal types I, II or III (I, II, or III), or naturally infected cats (N) clustered in the grid nodes 1 to 8 either together (type III- and atypical type-infected [node 4] as well as the type II and naturally infected cats [nodes 1 to 3 and 6 to 8]) or separately (cats infected with type I T. gondii [node 5]). Three cat groups were predicted using XYF-SKN, e.g. a cat group infected with non-canonical and type III T. gondii strains (A), a clonal type I infected group (I) and a naturally-infected cat group (N). Predicted cat groups are presented by different background colours of grid nodes, e. g A by red, I by green and N by blue. Figure (B) shows the number of group-specific sera within predicted clusters (A, I and N), further confirming that sera of naturally infected cats clustered mainly with type II reference sera. Figure (C) shows the number of group-specific sera within eight grid nodes in Figure (A).