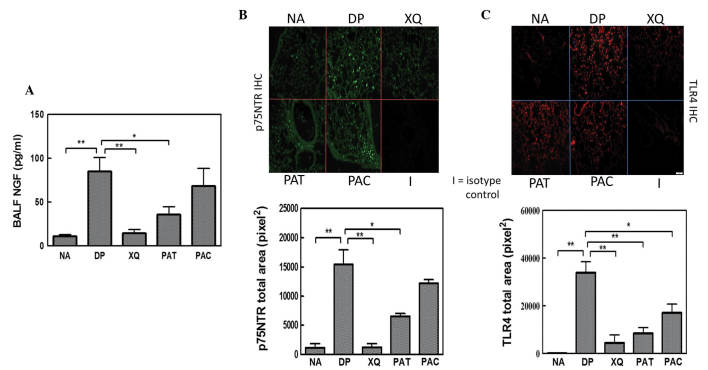
Figure 2.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunohistochemistry showing the inhibitory effects of Xiao-Qing-Long-Tang (XQLT) on Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Der p)-induced nerve growth factor (NGF)/p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR)/Toll receptor-like 4 (TLR4) expression in the lungs. Der p allergen significantly induced NGF/p75NTR/TLR4 expression in the lungs in the the allergen-challenged mice without oral XQLT (DP group). XQLT oral administration, particularly as a preventative strategy (PAT group), decreased (A) NGF, (B) p75NTR and (C) TLR4 expression. The average area of fluorescence density in immunohistochemistry was calculated from the fluorescence of 36–50 vision fields in each group. Values represent the mean ± standard deviation; n=6 mice for each group. P<0.01, statistics of all groups were versus group DP. NA, naive mice; XQ, mice with XQLT treatment, but without allergen challenge; PAC, post-allergy curing protocol group; BALF, broncho-alveolar lavage fluids. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.