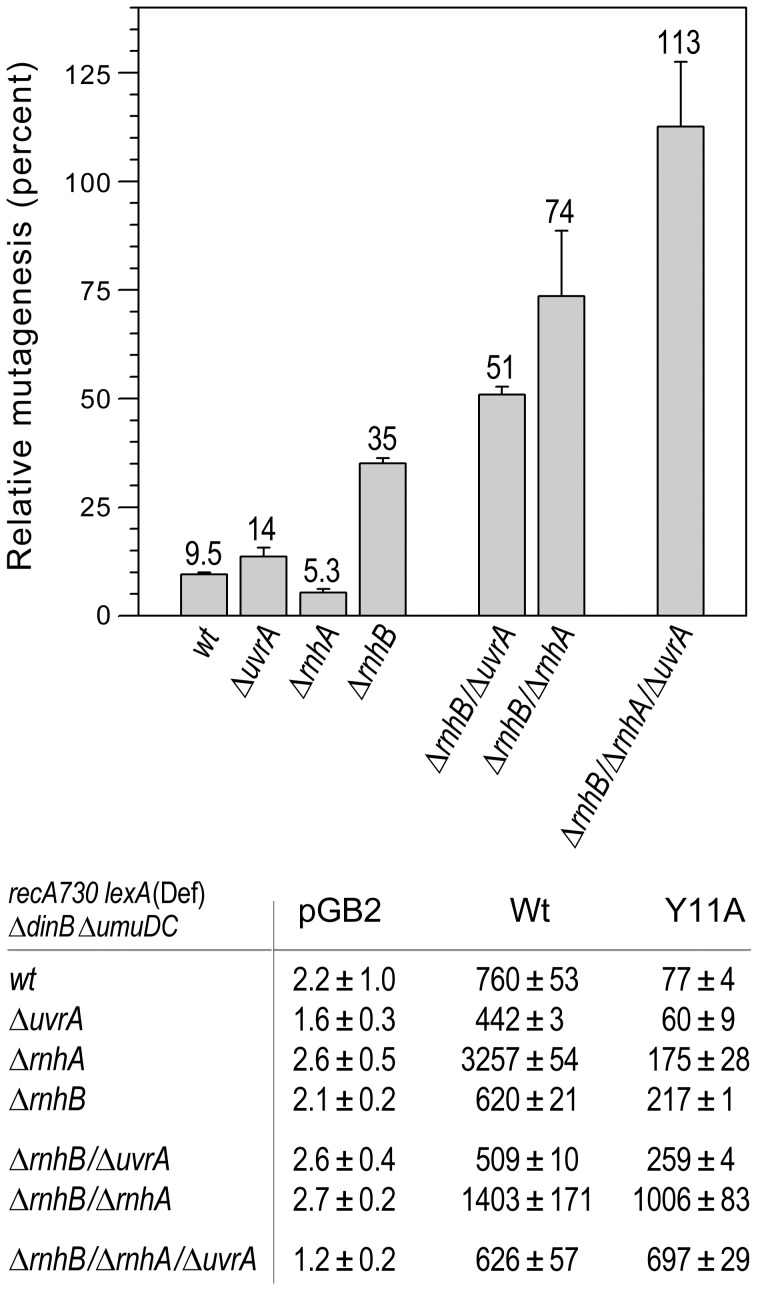
Figure 3. Effect of deleting rnhA, rnhB and/or uvrA alone, or in various combinations, on the extent of umuC_Y11A-dependent spontaneous mutagenesis in recA730 lexA(Def) ΔumuDC ΔdinB strains.
We constructed a series of isogenic recA730 lexA(Def) ΔdinB ΔumuDC strains with ΔrnhA, ΔrnhB or ΔuvrA alleles alone, or in various combinations and assayed pol V-dependent spontaneous mutagenesis in strains harboring plasmids expressing wild-type pol V or umuC_Y11A by assaying reversion of the hisG4 (ochre) allele. The data plotted on the graph represent the relative extent of spontaneous mutagenesis in cells expressing umuC_Y11A calculated as a percentage of the spontaneous mutagenesis in cells expressing wild-type pol V. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Standard errors were calculated taking into account variability in spontaneous mutagenesis in each strain. Data for the wild-type, ΔrnhA, ΔrnhB and the ΔrnhA ΔrnhB strains were taken from [11] and are shown for comparison. As clearly observed, in contrast to the ΔrnhA or ΔuvrA strains, which exhibit roughly the same extent of umuC_Y11A-dependent mutagenesis as the wild-type strain, the ΔrnhB strain exhibited significantly higher levels of spontaneous mutagenesis, suggesting that the rnhB-encoded RNase HII repair pathway is the primary defense against errant ribonucleotide incorporation in E.coli. However, in contrast to the rnhB + strains, deletion of either rnhA or uvrA in the ΔrnhB strain background leads to a further increase in umuC_Y11A-dependent spontaneous mutagenesis, suggesting that both enzymes participate in back-up pathways of ribonucleotide repair. Furthermore, umuC_Y11A-dependent spontaneous mutagenesis in the ΔrnhA ΔrnhB ΔuvrA triple mutant strain is actually higher than in the isogenic strain expressing wild-type pol V. These data imply that all major pathways specific for ribonucleotide repair are blocked in this strain background.