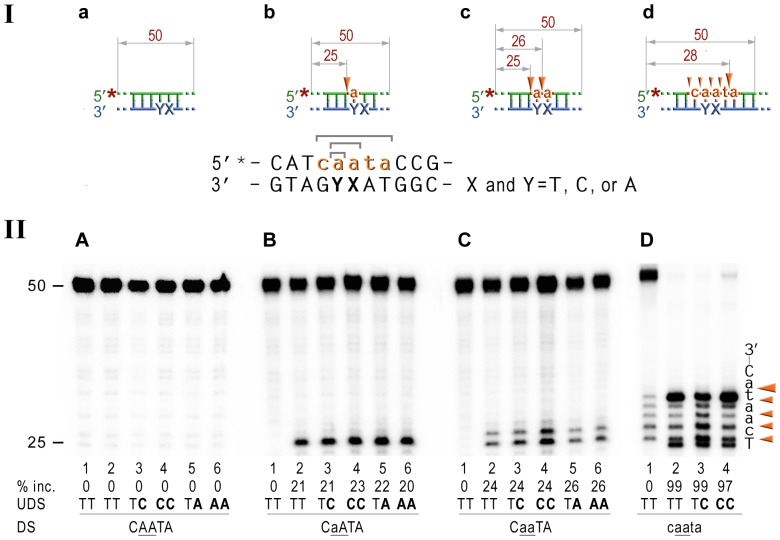
Figure 5. RNase HII cleavage reaction products generated using various DNA-RNA-DNA hybrid substrates.
I; Cartoon of the synthetic substrates used in the in vitro assays, with the sites of incision and expected product size indicated, along with the DNA sequence containing rNMP(s) and mismatched nucleotides. II; The 50-mer duplexes (10 nM) in which the modified strand was 5′ end-labeled (indicated by *), were incubated with Rnase HII for 60 min at 37°C. The DNA duplexes (panel A) as well as DNA-RNA-DNA hybrids containing either single rAMP (panel B), two consecutive rAMPs (panel C), or five rNMPs (panel D) were assayed. The reaction products were separated under denaturing conditions by 15% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). The efficiency of RNase HII-dependent incision was determined as a percentage of the radioactivity in the incised products relative to the total signal of the substrate (% inc.). The data below the gels are mean values calculated from at least two independent experiments. The DNA sequence containing rNMP(s) is shown alongside the gels where DNA and RNA are represented by uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively. Orange arrows indicate the cleavage sites. The in vitro assays confirm that E.coli RNase HII nicks the DNA backbone 5′ of ribonucleotides embedded in DNA and shows that the efficiency of the reaction is largely unaffected by base-mispairs.