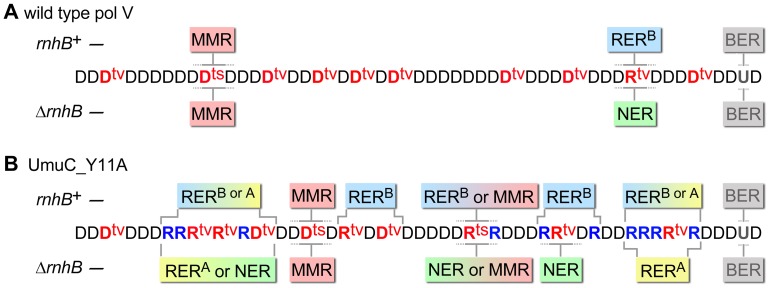
Figure 7. Various DNA repair pathways compete, cooperate, or substitute for each other in order to sanitize the E.coli chromosome from mispairs, uracils and incorporated rNMPs.
The cartoon helps to explain why spontaneous mutagenesis induced by wild-type pol V (A) differs from Y11A_UmuC-dependent mutagenesis (B) and illustrates the respective roles of MMR (red box), RERA (stands for RNase HI-initiated ribonucleotide excision repair and is indicated in yellow), RERB (RNase HII-initiated ribonucleotide excision repair, indicated in blue), NER (green), and BER (grey) (The competing pathways are indicated by boxes with gradient colors). Misincorporated nucleotides are shown in red (where ts are transitions, tv are transversions), correctly paired ribonucleotides are indicated in blue. For simplicity, all the transversions are shown refractory to MMR and NER while in reality they could be repaired by both pathways although less efficiently than transitions. Both wild-type and mutant pol V make frequent base-substitution errors. The transition mutations are rapidly repaired by MMR, while any errant ribonucleotides (correctly-paired or mispaired) are also efficiently removed by RERB. Ung-dependent BER only operates on dU, not rU, incorporated into the DNA and therefore has no role in RER. In contrast, NER is able to remove rNMPs misincorporated by either wild-type or mutant pol V. Since umuC_Y11A is able to incorporate multiple consecutive rNMPs into DNA, RER involving RNase HI is limited to strains expressing the pol V variant. RERB is normally required for highly efficient removal of errant ribonucleotides, however, in its absence the role of NER and RNase HI becomes apparent. The fact that the level of spontaneous mutagenesis in strains expressing umuC_Y11A with an “unlocked” sugar steric gate is 90% lower than mutagenesis in strains harboring wild-type pol V, implies that numerous errant ribonucleotides are very efficiently excised by the collaborative actions of rNMP-specific repair pathways which concomitantly remove mispaired dNMPs positioned within the repair patch (such as for example two Dtvs in the panel B). In the absence of RNase HI, RNase HII and NER proteins, the majority of the misincorporated rNMPs remains embedded in the chromosomal DNA. As a result, spontaneous mutagenesis in the ΔrnhA ΔrnhB ΔuvrA strain expressing umuC_Y11A is higher than in the isogenic strain expressing wild-type pol V.