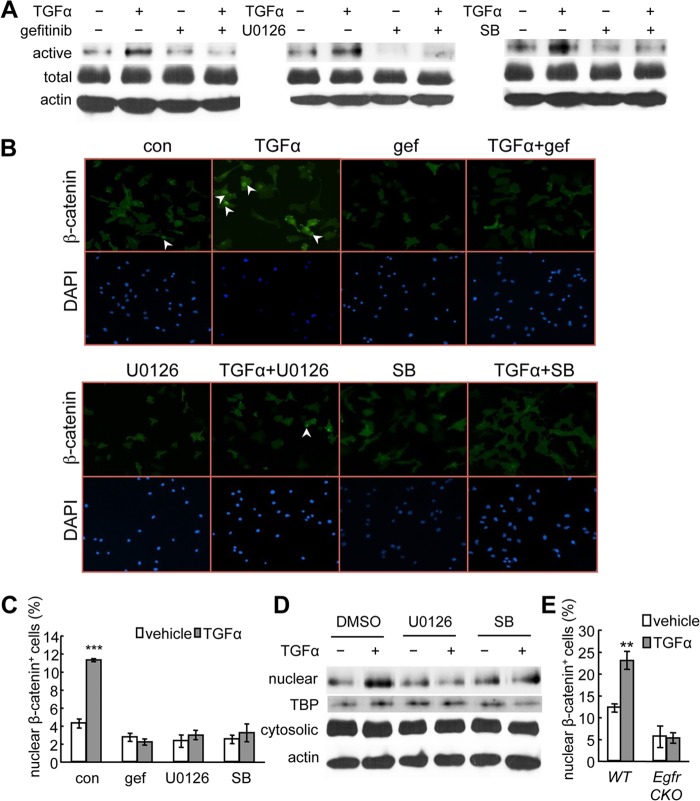
FIGURE 6.
TGFα activates β-catenin and stimulates its nuclear translocation in chondrocytes. A, rat primary chondrocyte cultures were pretreated with the indicated inhibitors followed by 48 h of TGFα treatment and subjected to immunoblot analyses of the active form of β-catenin (active), total β-catenin (total), or β-actin as internal control (actin). SB, SB203580. B and C, immunofluorescence was performed with rat primary chondrocytes to detect the nuclear accumulation of β-catenin after 24 h of TGFα treatment in the absence and presence of pathway-specific inhibitors. Representative images were shown in B. The percentages of cells with β-catenin nuclear staining were quantified in C. ***, p < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated control (con). gef, gefitinib. D, the nuclear and cytosolic fractions of rat primary chondrocytes treated with TGFα and MAPK inhibitors were processed for immunoblotting of β-catenin and its internal nuclear (TATA-binding protein (TBP)) and cytosolic (β-actin) controls. E, a similar immunofluorescence experiment was performed with mouse primary chondrocytes derived from WT and Egfr CKO mice. **, p < 0.01 versus vehicle-treated WT cells.