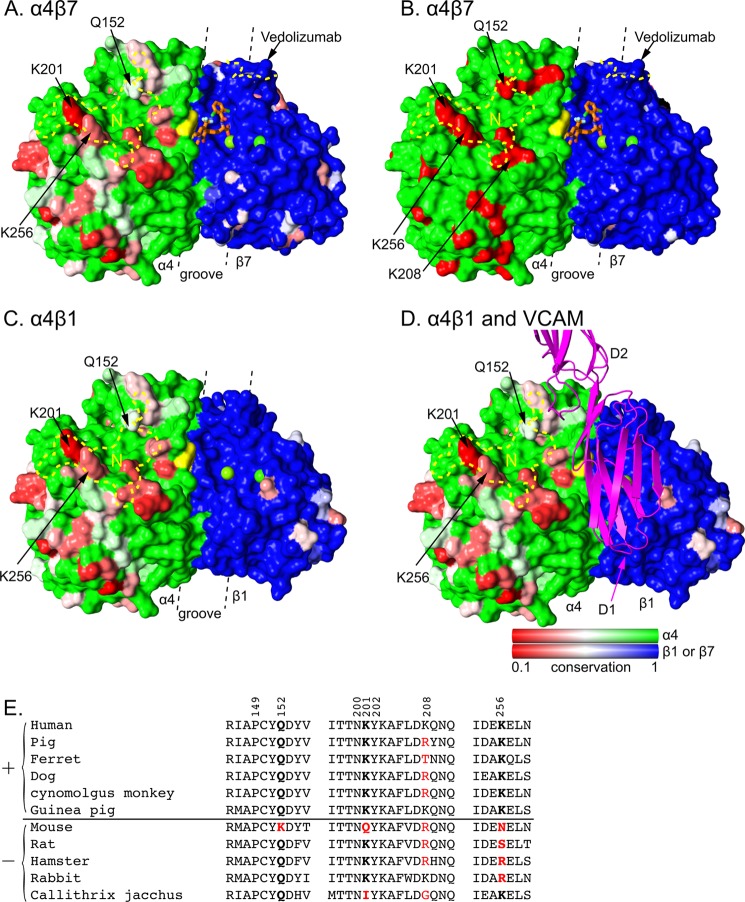
FIGURE 5.
Species-specific differences around the integrin α4β7 and α4β1 ligand-binding sites. Conservation on the solvent accessible surface is displayed from invariant (1, green or blue) to low (0.1, red) for A, C, and D using the species shown in panel E. In B, mouse-human sequence is shown as invariant (green or blue) or different (red). Invariant α and β subunit residues are shown in green and blue, respectively, to visualize the subunit interface. Additionally, invariant VCAM-binding α4 residues Tyr-187 and Trp-188 are in yellow and β subunit MIDAS and ADMIDAS metal ions are shown as green spheres. Antibody footprints are outlined in yellow dashes (N for natalizumab) and key antigenic residues are labeled. A small molecule antagonist bound to α4β7 is shown in stick with orange carbons (11). VCAM is shown in ribbon representation in the orientation found previously in docking to α4β7 (11). A–D are in identical orientations. The α4β1 model was made by superimposing the β1 βI domain from α5β1 (44) onto α4β7 (11). The location of the ligand binding groove is marked with dashed lines. Sequence conservation was calculated by AL2CO (51) with species equally weighted, using the sum of pairs measure with the BLOSUM62 matrix with normalization of the scoring matrix. There was no further normalization, so results for α4, β1, and β7 all use the same scale. E, sequence variation in the natalizumab epitope. Sequences are of species found to be positive (+) or negative (−) for natalizumab reactivity in European Medicines Agency filings. Residues in the epitope are numbered. Residues most important for species reactivity are in bold. Residues that differ from human are red.