FIGURE 1.
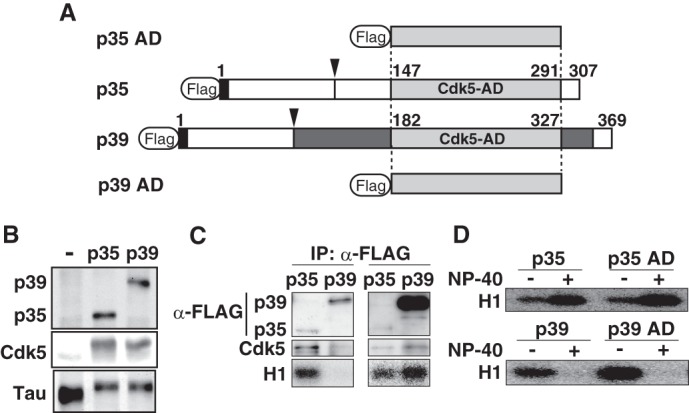
Different stability of p35-Cdk5 and p39-Cdk5 in nonionic detergent is caused by differences in the Cdk5-activation domain. A, schematic representation of full-length p35 and p39, and both C-terminal Cdk5-AD, p35 AD and p39 AD. p35 and p39 contain a Cdk5-AD (light gray) in the C-terminal region. The p35 AD and p39 AD consist of 145 and 146 amino acids, respectively, and share 72% identity. p39 has a Pro-rich sequence and additional residues flanking the Cdk5-AD (dark gray). The calpain cleavage site in p35 and p39 is indicated by the arrowhead. The extreme N-terminal nine amino acids (black), which include a myristoylation signal, are conserved between p35 and p39. B, kinase activity of p35-Cdk5 and p39-Cdk5 in HEK293 cells. The kinase activity of p35-Cdk5 and p39-Cdk5 was assessed by examining the phosphorylation-dependent upward shift of Tau, which was co-expressed and evaluated by immunoblotting (bottom panel). C, kinase activity of p35-Cdk5 and p39-Cdk5 expressed in HEK293 cells. p35 or p39 tagged with FLAG was expressed together with Cdk5 in HEK293 cells. p35-Cdk5 (left lanes) or p39-Cdk5 (right lanes) was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-FLAG (top panels) or anti-Cdk5 (middle panels) antibody. The kinase activity of immunoprecipitates was measured using histone H1 and [γ-32P]ATP as substrates. D, kinase activity of p35-Cdk5, p35 AD-Cdk5, p39-Cdk5, and p39 AD-Cdk5. p35-Cdk5 and p35 AD-Cdk5 were immunoprecipitated in the absence of Nonidet P-40, followed by measurement of histone H1 kinase activity in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 1% Nonidet P-40 (upper panel). The kinase activity of p39-Cdk5 and p39 AD-Cdk5 was also measured (lower panel).
