FIGURE 3.
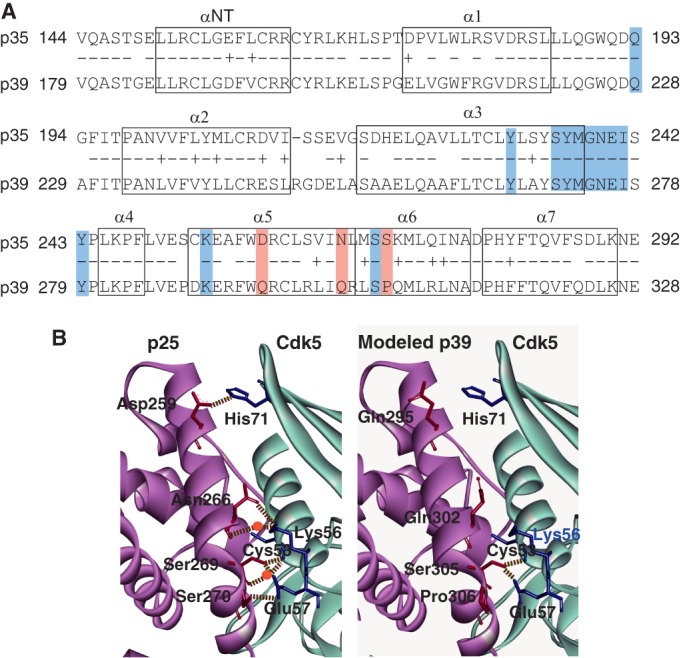
Hydrogen bond network between Cdk5 and p25 (p35 AD) or p39 AD. A, amino acid alignment and α-helix regions in p35 AD and p39 AD. Eight α-helices are indicated by boxes (23). Identical amino acids are indicated by −, and homologous amino acids are indicated by +. The amino acids that participate in the hydrogen bond network are shaded: the amino acids common to p35 and p39 are indicated in blue, and the three different amino acids are red. B, ribbon diagrams of the three-dimensional structure around the interface between Cdk5 and p25 (p35 AD) or p39 AD. The left panel is the crystal structure of p25 (A-chain)-Cdk5 (D-chain) registered in Protein Data Bank code 1UNH (25). p25 is represented by magenta, and Cdk5 is in light blue. The right panel is the three-dimensional structure of the corresponding region of p39 AD-Cdk5 predicted by in silico modeling; p39 AD is represented by magenta, and Cdk5 is in light blue. Hydrogen bonds are shown by dashed lines, and the water molecules that make a hydrogen bridge are indicated by red circles. Although Asp-259, Asn-266, and Ser-270 of p25 (p35 AD) form hydrogen bonds or hydrogen bridges with His-71, Lys-56, and Glu-57 of Cdk5, respectively, the corresponding amino acids, Gln-295, Gln-302, and Pro-306, of p39 AD do not form hydrogen bond networks with any amino acids of Cdk5.
