FIGURE 4.
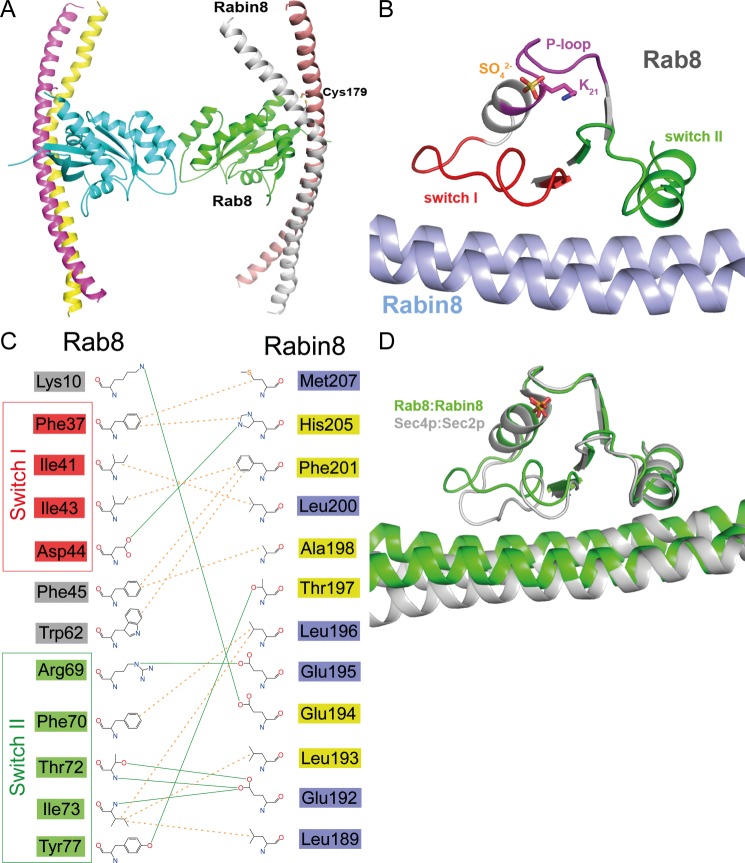
Structure of the nucleotide-free Rab8·Rabin8 complex. A, overall structure of the nucleotide-free Rab8·Rabin8 complex. Remarkably, the Cys-179 residues of both Rabin8 chains form a disulfide bond, stabilizing the dimer. B, binding interface of the nucleotide-free Rab8·Rabin8 complex. Lys-21 interacts with a sulfate ion. The binding of Rab8 to Rabin8 is via the interaction between the switch I and switch II domains of Rab8 and residues 187–212 of Rabin8. C, schematic representation of the binding interface of Rab8·Rabin8. The residues from switch I and switch II of Rab8 are colored red and green, respectively. The residues of Rabin8 are colored yellow or blue depending on their chain ID. D, superposition of nucleotide-free Rab8·Rabin8 with the Sec2·Sec4 complex. There is no difference in switch II between these two complexes, whereas switch I binds to the GEF differently. This could be the reason for the higher GEF activity of Sec2 compared with Rabin8 and GRAB.