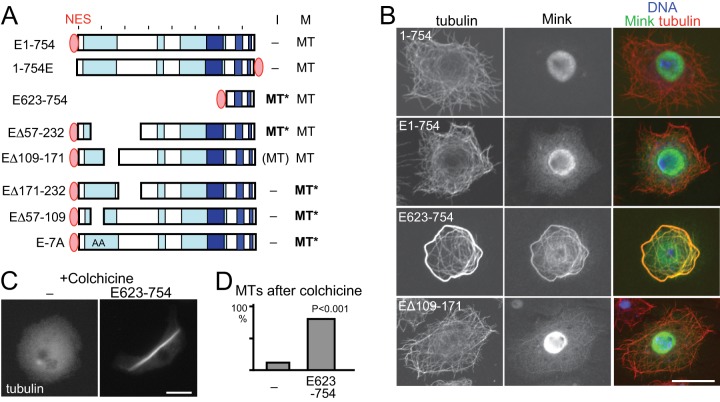
Fig. 5.
Misregulation of Mink disrupts microtubule organization. A, a summary of the subcellular localization of NES-fused Mink and truncated proteins. “MT” in bold and followed by an asterisk indicates that Mink localized to microtubules and induced abnormal microtubule organization. B, confocal images of immunostained GFP-Mink, GFP-NES-Mink, GFP-NES-Mink (623–754), and GFP-NES-Mink (Δ109–171). GFP-NES-Mink localized in the cytoplasm without associating with microtubules. The spindle binding domain (623–754) fused with GFP-NES in the cytoplasm associated with microtubules and induced microtubule bundling. Bar = 10 μm. C, microtubule stability in cells with or without expression of GFP-NES-Mink (623–754). Cells were immunostained for α-tubulin after incubation with colchicine. D, the frequencies of cells with considerable amounts of microtubules after incubation with colchicine. Cells expressing GFP-NES-Mink (623–754) and cells not expressing GFP (–) in the same transfected cell population were counted for microtubule morphology. The differences are significant between them (p < 0.001, Chi-square test).