Fig. 7.
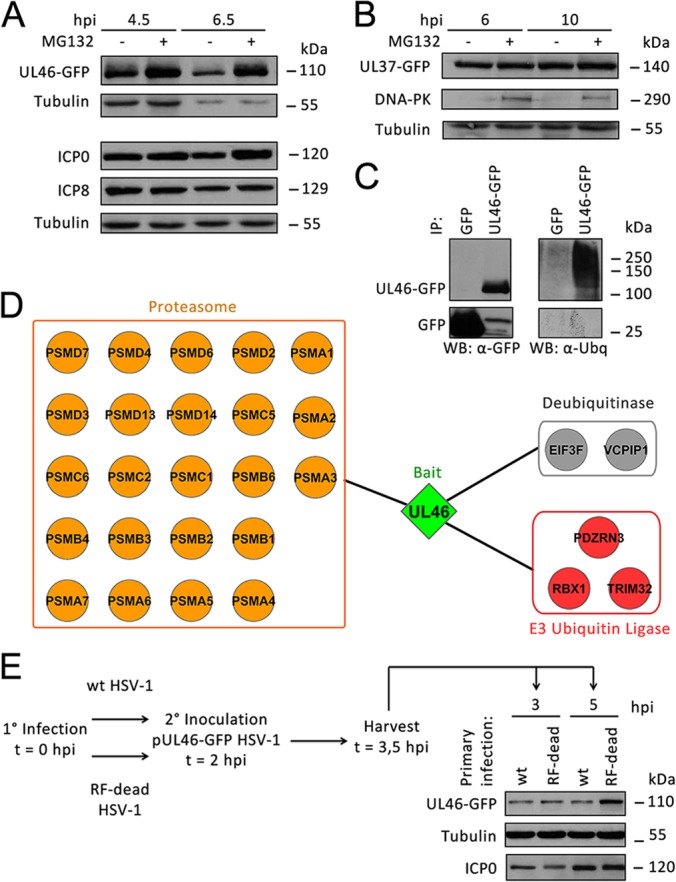
pUL46 is partially degraded by ICP0 in a proteasome-dependent manner during HSV-1 infection. A, Proteasomal degradation of pUL46. HFFs were infected with pUL46-GFP HSV-1 at an MOI of 10, treated with mock or 10 μm MG132 at 1 hpi, and harvested at 4.5 and 6.5 hpi. Whole cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE. B, pUL37-GFP is not degraded in a proteasome-dependent manner. HFFs were infected with pUL37-GFP HSV-1 at an MOI of 10, treated with mock or 10 μm MG132 at 1 hpi, and harvested at 6 and 10 hpi. C, pUL46 is ubiquitinated. HFFs were infected with HSV1-UL46-GFP or GFP HSV-1 at an MOI of 10, treated with 10 μm MG132 at 1 hpi, and harvested at 8 hpi. pUL46-GFP or GFP was immunoaffinity isolated using a higher stringency buffer, and eluates were separated by SDS-PAGE. D, Several proteasome subunits associate with pUL46 in infected cells treated with MG132. HFFs were infected with pUL46-GFP HSV-1 at an MOI of 10, treated with 10 μm MG132 at 1 hpi, and harvested at 6 hpi. Proteins co-isolated with pUL46-GFP were analyzed by nLC-MS/MS and visualized by Cytoscape. E, Catalytically active ICP0 is responsible for degradation of pUL46. HFFs were primarily infected with either wild-type or ICP0 RF-dead HSV-1 at an MOI of 10. At 2 hpi, HFFs were superinfected with pUL46-GFP HSV-1 at an MOI of 40, and cells were harvested at 3 and 5 hpi. Whole cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE.
