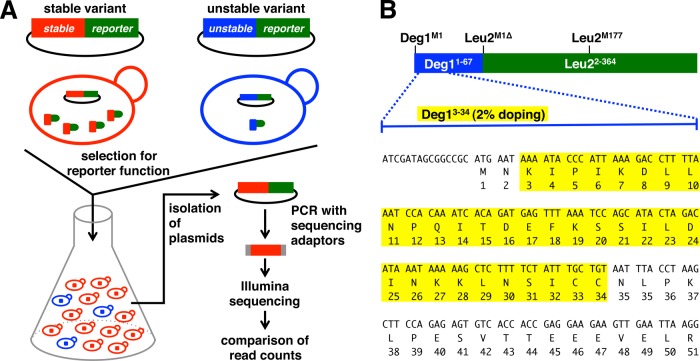
Fig. 1.
Overview of Stable-seq. A, variants of a protein are fused to a biosynthetic enzyme that serves as a reporter protein. The variants determine the stability of the reporter, and thereby the growth rate of yeast. A library of plasmids encoding variants fused to such a reporter is constructed, transformed into yeast, and selected for reporter function. Plasmids isolated before and after selection are subjected to high-throughput sequencing. The change in the frequency of each variant is a measure of its stability. B, library design and sequence of Deg1. Residues 3–34 selected for doping to generate a Deg1 mutant library are highlighted in yellow.