Figure 6.
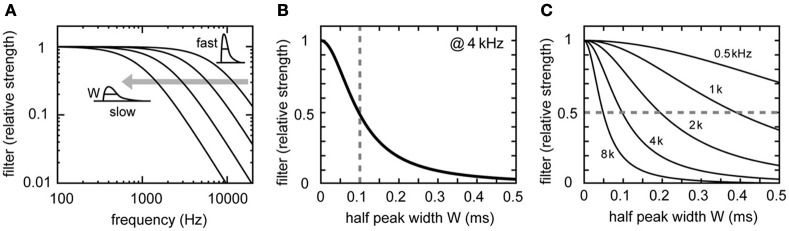
Frequency properties of the synaptic filter. (A) Fourier transform |Fα(f)| of the synaptic filter α(t) (see Table 1). Normalized curves with W = 0.05, 0.10, 0.20, and 0.40 are shown. The synaptic filter becomes more likely to reduce high frequency components as the synaptic time scale W becomes smaller. (B) Synaptic filter at 4 kHz showing non-linear dependence on W. The vertical broken gray line in (B) shows the default parameter (W = 0.1) used in our simulations. (C) Comparison of synaptic filters at different sound stimulus frequencies fs (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 kHz). Filter strength exceeds 0.5 (broken gray line), if and only if the inequality W < k/(2πfs) is satisfied. Note that this critical W-value is dependent on the frequency.
