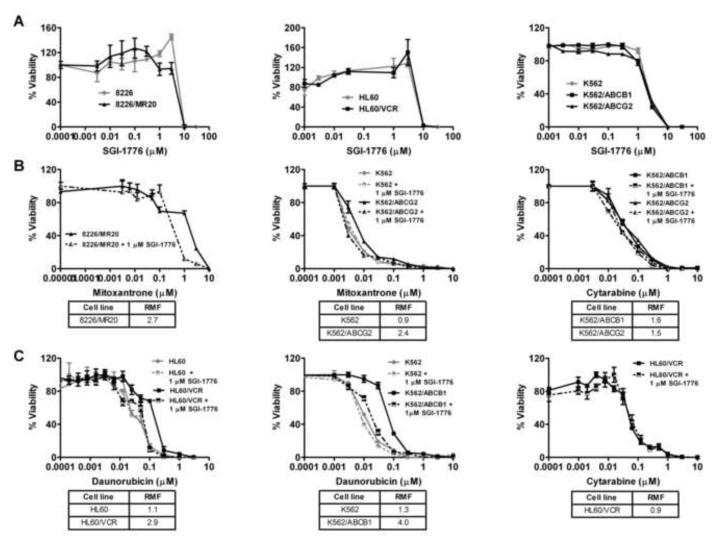
Figure 3.
A. SGI-1776 is similarly cytotoxic to cells expressing ABCG2 or ABCB1 and parental cells. 8226/MR20, HL60/VCR, K562/ABCG2 and K562/ABCB1 cells, expressing ABCG2 or ABCB1, and HL60, 8226 and K562 parental cells in log growth phase were cultured in 96-well plates at a density of 1× 103 cells per well in the presence of SGI-1776 in increasing concentrations for 96 hours. Viable cells were subsequently quantified using the WST-1 assay as detailed in Materials and Methods. Results are shown as mean ± SEM (n=6). B SGI-1776 (1μM) sensitizes ABCG2-overexpressing cells to ABCG2 substrate, but not non-substrate, drugs. 8226/MR20 and K562/ABCG2 cells, expressing ABCG2, and K562 parental cells were plated with mitoxantrone or cytarabine at increasing concentrations in the presence and absence of 1 μM SGI-1776. Resistance modifying factors (RMF) were calculated and are shown below the graphs. C. SGI-1776 sensitizes ABCB1-overexpressing, but not parental, cells to ABCB1-substrate, but not non-substrate, drugs. HL60/VCR and K562/ABCB1, expressing ABCB1, and their respective parental cell lines were plated as above with daunorubicin or cytarabine in increasing concentrations in the presence and absence of 1 μM SGI-1776, and viable cells were subsequently quantified using the WST-1 assay. The experiment was repeated three times and means ± SEM are shown. IC50s in the presence and absence of SGI-1776 were derived, and RMFs for 1 μM SGI-1776 were then calculated for each cell line as detailed in Materials and Methods. RMF values are shown below the graphs.