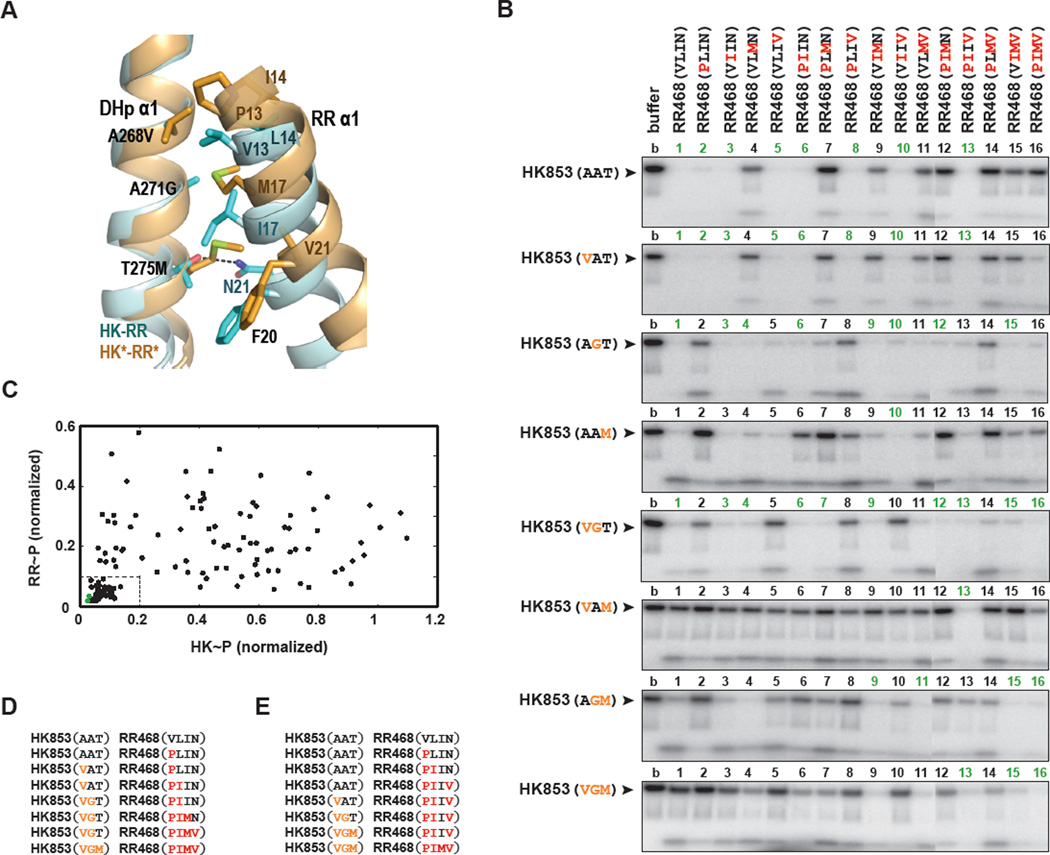
Figure 6. Phosphotransfer between all possible mutational intermediates separating HK-RR and HK*-RR*.
(A) Superposition of HK-RR (in cyan) and HK*-RR* (in orange) complexes highlighting how mutations in DHp α1 (A268V, A271G and T275M) affect interactions with mutations in RR α1 (V13P, L14I, I17M and N21V) and F20. A dashed line represents a polar interaction between N21 and T275 in the HK-RR complex. Also see Figures S4–S6. (B) Phosphotransfer assays for wild-type HK853 and HK853 harboring all possible combinations of one, two, or three PhoR-like specificity substitutions present in HK853** (A268V, A271G and T275M). Each lane represents the incubation of the indicated autophosphorylated kinase with the indicated response regulator for 15 seconds at room temperature. Reactions 1–11 and 12–16 were run on separate SDS-PAGE gels; the resulting phosphorimages were contrasted identically and stitched together. (C) The histidine kinase (HK) and response regulator (RR) bands from the phosphotransfer experiments in panel B were quantified and plotted. For each mutational pairing, the x-axis value indicates the intensity of the autophosphorylated HK band (HK~P) normalized to the intensity of the autophosphorylated kinase band and the y-axis value indicates the intensity of the phosphorylated response regulator band (RR~P). In each case, band intensities were normalized to the intensity of the autophosphorylated kinase incubated without response regulator (lane 1 of each gel in panel B). Green points indicate the pairs HK853-RR468 and HK853*-RR468*. The box in the lower left indicates pairings deemed functional; a low level of both the kinase and regulator bands reflects efficient phosphotransfer and dephosphorylation. The 43 functional pairings are underlined in panel B. (D) One example of a mutational path from the wild-type to the rewired complex in which each intermediate state is functional. (E) An example of a mutational path in which all mutations to the kinase occur in three successive steps.