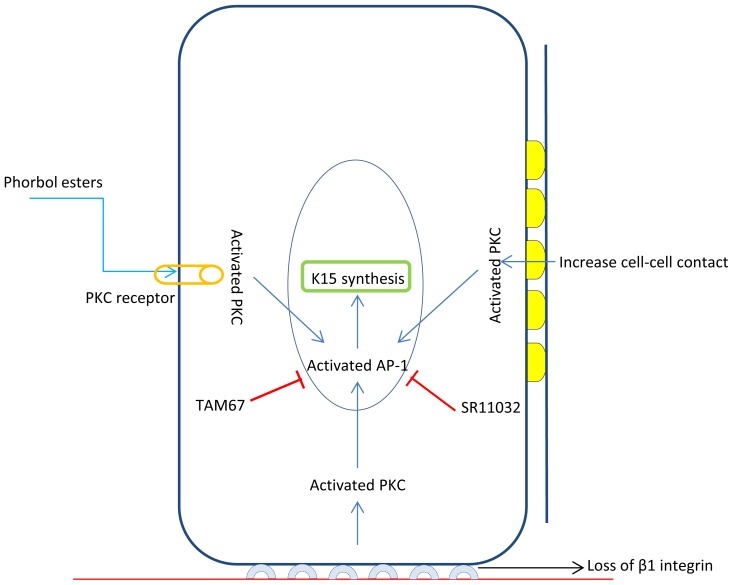
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the molecular signalling responsible for the differentiation-specific induction of Keratin 15 (K15) expression. Based on our previously published data we propose that K15, although normally a basal-specific keratin, can be induced in differentiating keratinocytes via Protein Kinase-C (PKC)/AP-1 pathway. Differentiation-specific signals, such as loss of cell-surface β1 integrin receptors, increased cell-cell interactions or exposure to tumour-promoter phorbol esters, activate the endogenous PKC signalling, which results in activation of downstream transcription factors AP-1, which in turn induce K15 gene transcription. Blocking the activation of AP-1 by specific inhibitor, SR11302, or by dominant negative form of c-Jun, TAM67, inhibits the transcriptional induction of K15 [61].