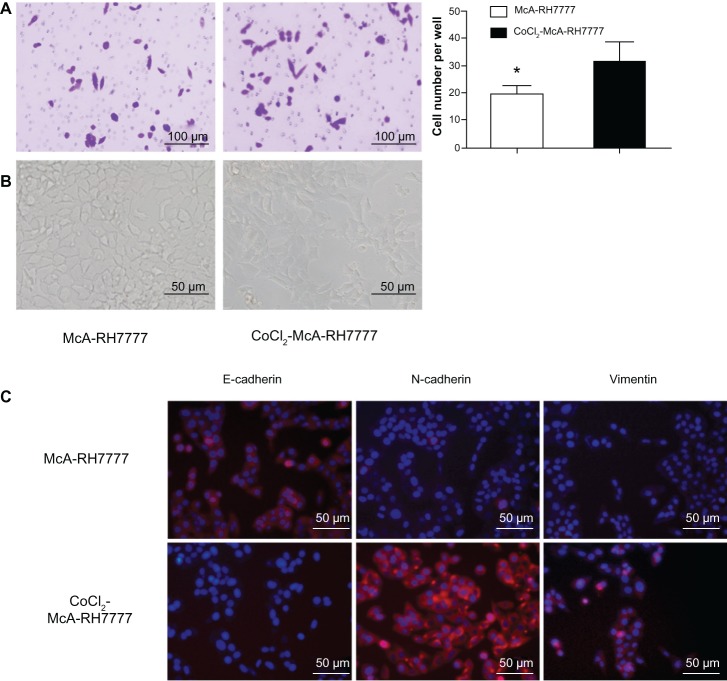
Figure 2.
McA-RH7777 cells after CoCl2 treatment exhibited the properties of enhanced invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition.
Notes: (A) CoCl2-treated McA-RH7777 cells showed a significant increase in cell invasion capacity compared with McA-RH7777 control cells. *P<0.05. (B) CoCl2-treated McA-RH7777 cells were morphologically distinct from the typical epithelial appearance of McA-RH7777 cells, showing a spindle shape with less cell–cell adhesion. (C) E-cadherin expression was reduced, but the expression of N-cadherin and vimentin was increased in CoCl2-treated McA-RH7777 cells relative to McA-RH7777 cells; this was examined by immunofluorescence.
Abbreviation: CoCl2, cobalt chloride.