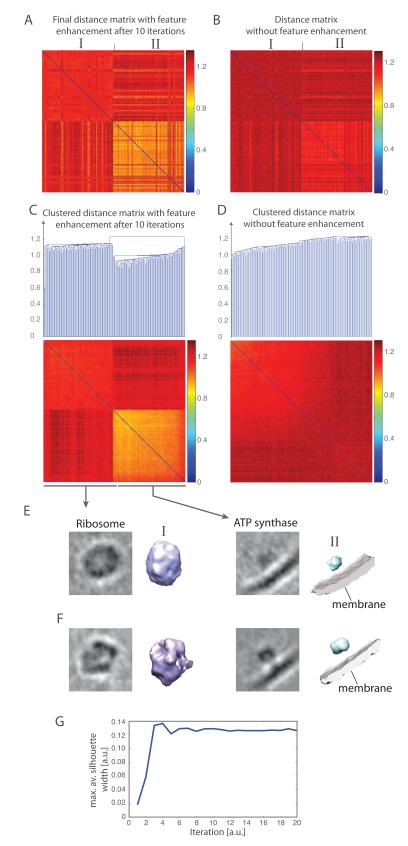
Figure 7.
Reference-free classification of 200 experimental subtomograms, extracted from a whole cell cryo-electron tomogram of L. interrogans (Beck et al., 2009). (A) Distance matrix after 10 iterations of reference-free subtomogram classification with the feature enhancement weight . The order of subtomograms is based on the result of template matching. The distance matrix is calculated using the feature enhancement weight. (B) Distance matrix calculated without feature enhancement weight after all subtomograms are aligned to the corresponding subtomograms with the highest matching score in template matching (Best et al., 2007). The order of subtomograms is identical to those in panel A. (C) Clustered distance matrix after 10 iterations of the reference-free classification process. Two different clusters are detected by the automatic cutoff detection, differentiating the ATP synthase complexes from the ribosome complexes. (D) Clustering of distance matrix as shown in panel B. The clustering into the two subgroups fails without feature enhancement and reference-free classification. (E) Averaged subtomograms after iterative classification. Shown are slices through the averaged subtomograms and the isosurface of the averaged subtomograms of each cluster. (F) Averaged subtomograms when all the subtomograms in each determined cluster are aligned to the respective ground truth template. Shown are slices through the averaged subtomograms and the isosurace of the averaged subtomograms. (G) Convergence of the classification process. The maximal average Silhouette width is calculated from the resulting subtomogram clusters at each iteration of the classification process. The convergence is reached when the maximal average Silhouette width reaches a plateau with increasing iterations.