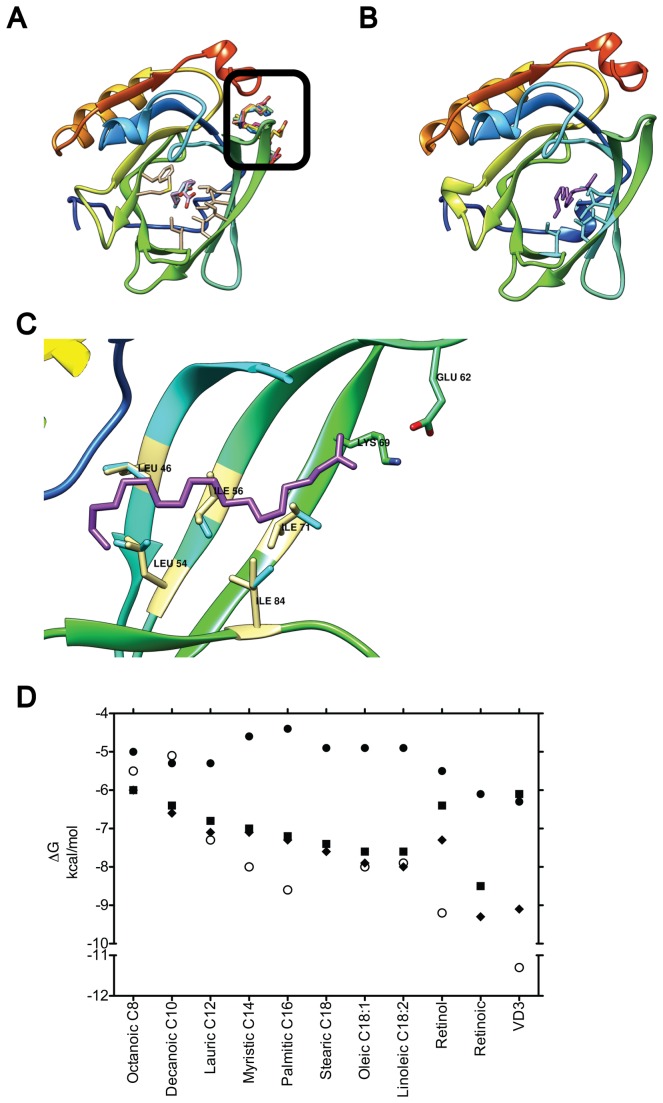
Figure 2. Effect of residue flexibility on fatty acid binding.
(A) Docking to a rigid 2BLG allows only the three smallest lipids into the calyx (shown superposed in white, light blue and light purple), while excluding longer fatty acids to Site C (black square, fatty acids in different colors). The seven binding residues in the calyx are shown in light yellow. When five of these residues were allowed flexibility all fatty acids bind the calyx. Stearic acid (purple) is shown bound in (B) and (C) in a full BLG top down view and a side view magnification of the calyx, respectively. In (C) the five flexible residues (blue) are shown aligned to their XRD counterpart (light yellow) to highlight movements that enable docking. (D) Plot of binding energy from docking vs. ligand using the monomeric empty, 2BLG, either rigid (black circles) or with 5 (black squares) or 7 (black triangles) flexible residues. Experimentally determined energies are shown for comparison (open circles). Fatty acids are sorted as in Figure 1C.