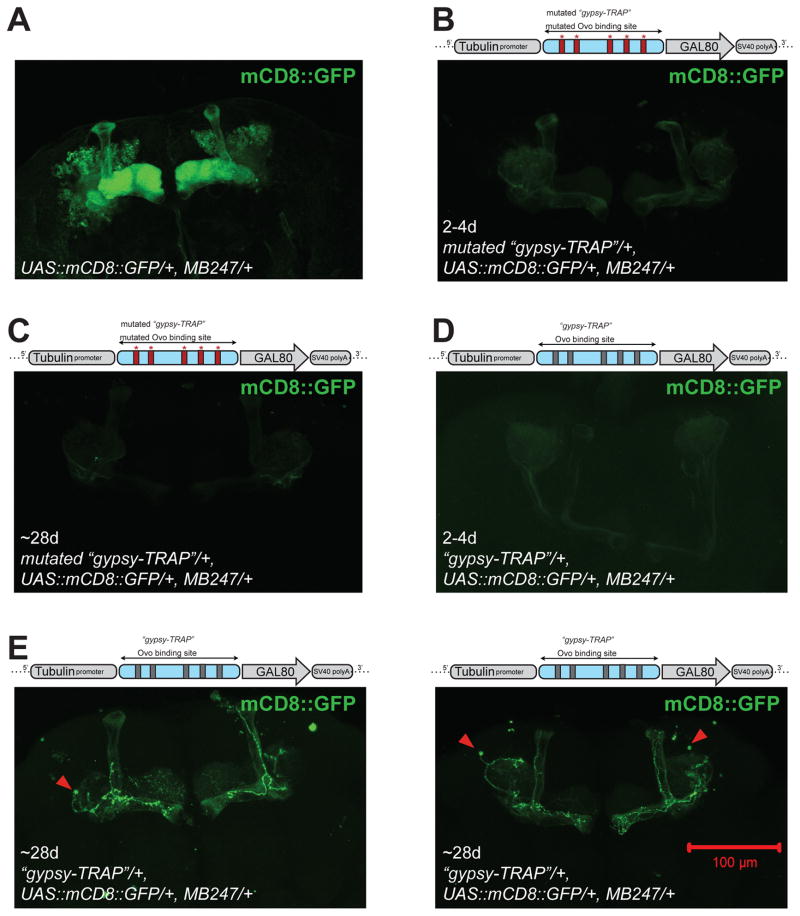
Figure 2. “Gypsy-TRAP” reporter detects de novo integration in neurons in aged animals.
A ~500bp fragment from the ovo regulatory region containing 5 Ovo binding sites is inserted between Tub promoter and GAL80 gene. A mutated “gypsy-TRAP” construct contains mutations that disrupt each of the 5 Ovo binding sites. In the absence of gypsy insertions, GAL80 expression suppresses GAL4, and UAS::mCD8::GFP is not expressed. In the presence of gypsy integration into the “gypsy-TRAP”, GAL80 expression is blocked, and UAS::mCD8::GFP is turned on (see Fig. S2). (A) Approximately 800 mushroom body Kenyon cell neurons per brain hemisphere are labeled by MB247-GAL4-driven UAS::mCD8::GFP. (B) An example brain from 2–4-day old mutated “gypsy-TRAP”; UAS::mCD8::GFP/+; MB247/+. No GFP labeled neurons seen. (C) An example brain from ~28-day old mutated “gypsy-TRAP”;UAS::mCD8::GFP/+; MB247/+. No GFP labeled neurons seen. (D) An example brain from ~2–4-day old “gypsy-TRAP”; UAS::mCD8::GFP/+; MB247/+. No GFP labeled neurons seen. (E) Example brains from ~28-day old “gypsy-TRAP”; UAS::mCD8::GFP/+; MB247/+. Several GFP-labeled MB neurons seen in each brain. See Table S1 and Fig. S2 for statistical summary and additional example images.