Fig. 3.
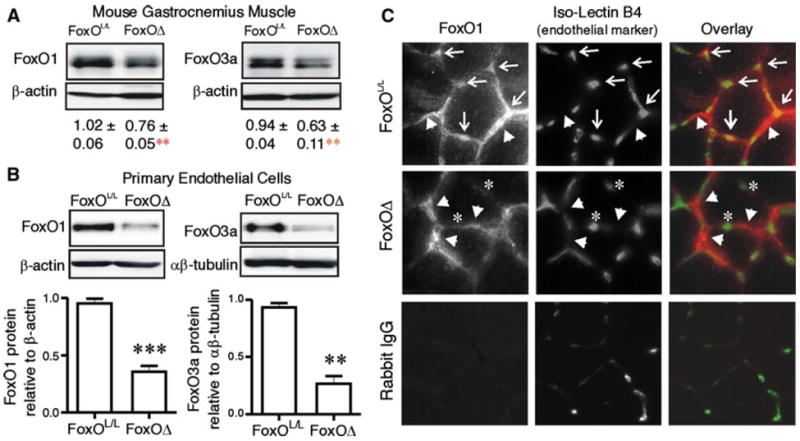
FoxO1 and FoxO3a deletion occur in skeletal muscle microvascular endothelial cells of FoxOΔ mice. FoxO1 and FoxO3a levels were measured by Western blotting on protein extracts of gastrocnemius muscles a harvested from 6 week old FoxOL/L and FoxOΔ mice. Protein level relative to β-actin is expressed as mean ± SEM. Differences vs. FoxOL/L are **p = 0.01 (n = 4–7 per group). FoxO1 and FoxO3a levels were assessed by Western blotting on protein extracts of microvascular endothelial cells b isolated from skeletal muscle of FoxOL/L and FoxOΔ mice. ***p < 0.0001 and **p < 0.01 (n = 3 to 4 independent cell isolations from a total of 9 mice per group). Cross-sections of TA/EDL muscles (4 days post femoral artery ligation) were immuostained c for FoxO1 (red) and Isolectin B4 (green). Arrows indicate capillaries positive for FoxO1 staining and arrowheads indicate myocyte/interstitial cell-associated FoxO1 immunoreactivity. Notably, FoxO1 staining did not overlap with Isolectin B4 staining in muscle cross-sections of FoxOΔ mice; asterisks highlight representative capillaries that do not exhibit FoxO1 immunoreactivity. Immunostaining of a FoxOL/L muscle section with normal rabbit IgG as a negative control for the FoxO1 antibody is shown in the bottom left hand panel
