Fig 4.
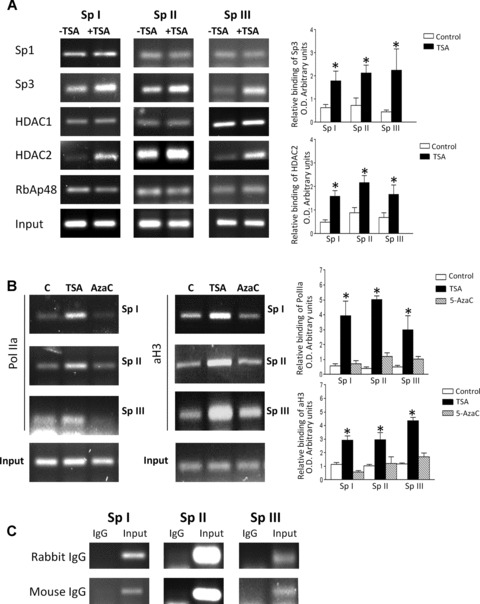
ChIP analysis confirms that the SpI-III (GC) binding sites within the RIIα promoter bind multi-protein complexes containing Sp1, Sp3, HDACS 1 and 2 and RbAp48 in vivo in human myometrial cells. Human myometrial cells were treated in the absence or presence of TSA (330 nM) or 5-AzaC (100 μM) for 6 hrs and ChIP analysis carried out as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Sp1, Sp3, HDAC1 and 2 and RbAp48 antibodies specifically precipitated PCR amplicons associated with the three Sp I-III (GC) cis-elements within the RIIα promoter. Incubation of myometrial cells with TSA resulted in increased binding of Sp3 and HDAC2 to the three Sp I-III (GC) sites. Data were obtained from three individual myometrial cell preparations analysed in triplicate and are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of the relative binding after correcting for Input (I) as a loading control. *P < 0.05 Student’s t-test (n = 9) for TSA treated compared to control. (B) Incubation of myometrial cells with TSA resulted in increased binding of acetylated Histone 3 (aH3) and PolIIa to the three Sp I-III (GC) sites; no increase in binding was observed for 5-AzaC. Data were obtained from three individual myometrial cell preparations analysed in triplicate (n = 9) and are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of the relative binding after correcting for Input. In each instance treatment with TSA resulted in a significant increase in binding compared to control or 5-AzaC treatment. *P < 0.05 Student’s t-test. (C) Rabbit and Mouse IgG controls indicated the specificity of all pull-downs.
