2.
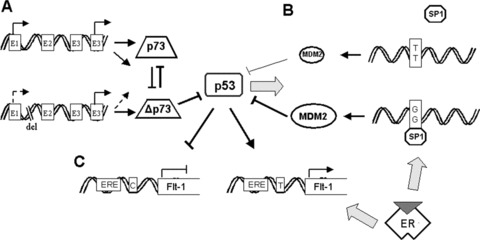
Polymorphisms in p53 pathways. (A) Role of p73 polymorphism. The presence of 73 bp deletion in the first intron of the TP73 gene is associated with lower levels of p73 but do not affect expression of Δp73 resulting in increased ratio of TAp73/ATAp73 forms, favouring p73 oncogenic variants. (B) Role of MDM2 SNP309. Single nucleotide polymorphism 309 in a region of the MDM2 promoter increases the affinity of the transcriptional activator Sp1, which along with active oestrogen receptors (ER) and genotoxic stress, was found to attenuate the p53 pathways resulting in the acceleration of tumour formation. (C) Role of RE polymorphisms. C to T SNP at the Flt-1 promoter creates a p53 binding site resulting in p53-dependent up-regulation of Flt-1 transcription in human cells. Active oestrogen receptor signalling considerably enhances this effect.
