2.
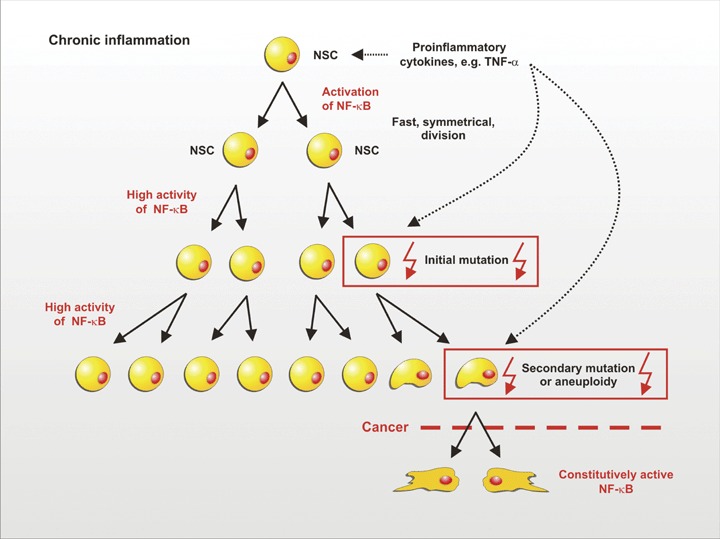
Model for the correlation between chronic inflammation, symmetric division of NSCs and cancer. In chronic inflammation, NSCs are permanently exposed to proliferation-inducing stimuli such as TNF-α. The ensuing rapid proliferation entails a much higher risk of mutation than slow cell division. Initial mutations could easily be propagated as a result of the fast symmetric division. Secondary mutations then may lead to constitutive NF-κB activity, aneuploidy and finally to cancer.
