6.
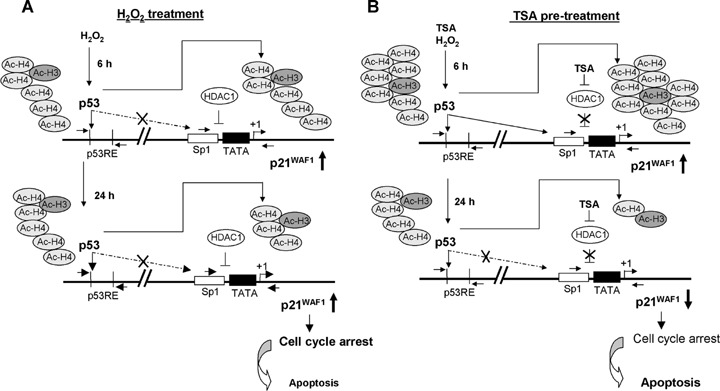
Mechanistic model to the action of H2O2 and TSA in oxidative-damaged HCT116 p53+/+ colorectal cancer cells. (A) H2O2 exposure causes a p53-induced transcriptional activation of p21WAF1 expression in association with acH4 by directly interacting especially with the p53 responsible element.(B) The combination of this DNA-damage pathway with TSA pre-treatment resulted in time-dependent effects on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis characterized as early and late responses.Firstly, TSA pre-treatment enables p53 to bind not only on the p53 RE but similarly on the Sp1 site of the p21WAF1 promoter by simultaneous displacement of HDAC1 and strengthened binding of acetylated H4, especially at the Sp1 site.Secondly, binding of p53 and therefore of acetylated H4 on the Sp1 site is significantly decreased in the late response as a consequence of TSA pre-treatment. This allows the cells to enter the cell cycle again and simultaneously to switch cells into apoptosis.
