Fig. 1.
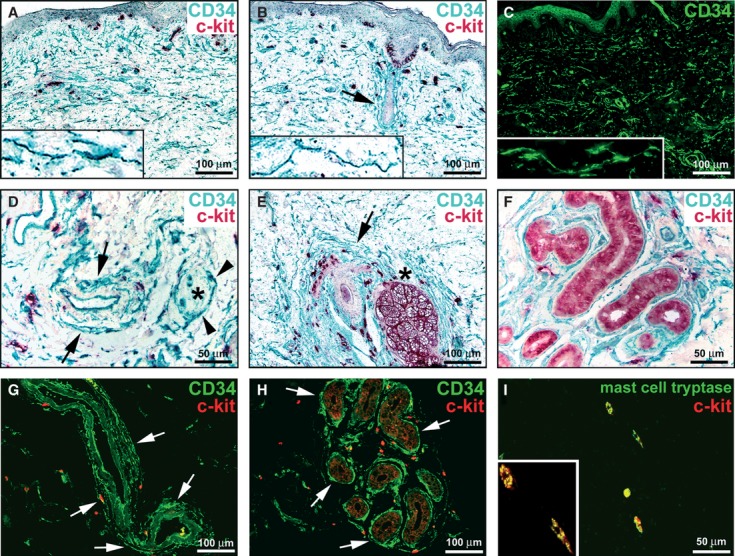
Normal skin, immunohistochemistry. (A, B, D–F) Double immunoenzymatic labelling for CD34 and c-kit with horseradish peroxidase (green) and alkaline phosphatase (red) detection systems respectively. (C) CD34 immunofluorescence labelling. (G and H) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (green) and c-kit (red). (I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for mast cell tryptase (green) and c-kit (red). (A–H) Dermal interstitial cells, presumably telocytes and endothelial cells display CD34-immunoreactivity. The CD34-positive cells do not display c-kit-immunoreactivity. In the papillary and reticular dermis, telocytes form an interstitial network (A–C). Telocytes have an elongated shape with an oval or triangular body and two or three long and thin cell processes with knobs/dilations along their length (A–C, higher magnification view in insets). Telocytes form a thin and almost continuous layer encircling arterioles (D and G, arrows). A nerve [denoted by an asterisk in (D)] is surrounded by telocytes (arrowheads). Telocytes make an almost continuous multilayered sheath around hair follicles (B and E, arrows), sebaceous glands (E, asterisk) and the secretory and excretory portions of eccrine sweat glands (F and H, arrows). Many c-kit-positive cells, round or oval in shape, are observed in the dermis, often in close contact with telocytes (A, B, D-H). Melanocytes (B) and epithelial cells of sebaceous (E) and sweat (F, H) glands are c-kit-immunoreactive. (I) The c-kit-positive cells show mast cell tryptase immunoreactivity. A higher magnification view of two double-positive mast cells is shown in the inset. Scale bars are indicated in each panel.
