Fig 2.
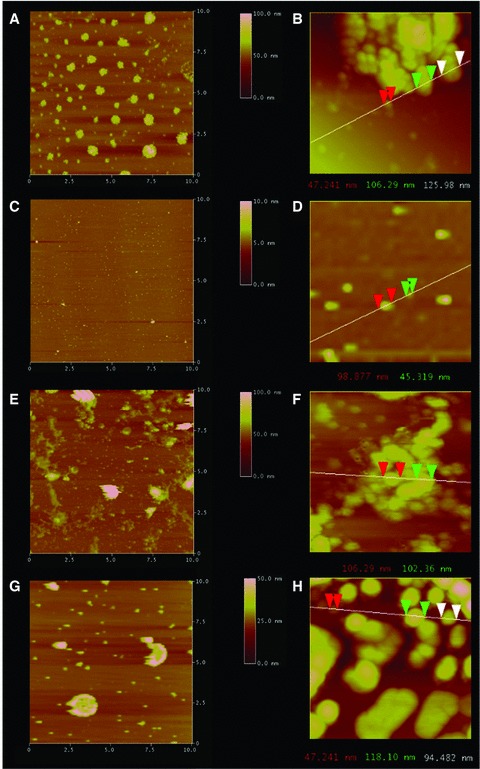
Representative AFM micrographs demonstrating LPC containing t-/v-SNARE proteoliposome complexes fail to dissociate in the presence of NSF–ATP. Exposure of cholesterol-associated t-SNARE and v-SNARE liposome mixtures (A, B), low and high magnification to NSF–ATP results in liposome dissociation as demonstrated in (C) at low magnification and (D) at higher magnification. In contrast, LPC-associated t-/v-SNARE liposomes (E, F) remain clustered (G, H) following exposure to NSF–ATP. The left column (A, C, E, G) representing low-resolution images are all 10 χ 10 μm. Similarly, the right column (B, D, F, H) representing high-resolution images are all approximately 1 χ 1 μm. Note the NSF–ATP induced t-/v-SNARE disassembly and the resultant dissociation of the cholesterol containing vesicles in (C) compared to (A), and in (D) compared to (B). As opposed to cholesterol, the NSF–ATP induced inhibition of t-/v-SNARE disassembly and the resultant inhibition in dissociation of the LPC containing vesicles in (G) compared to (E), and in (H) compared to (F), is demonstrated.
