Fig 4.
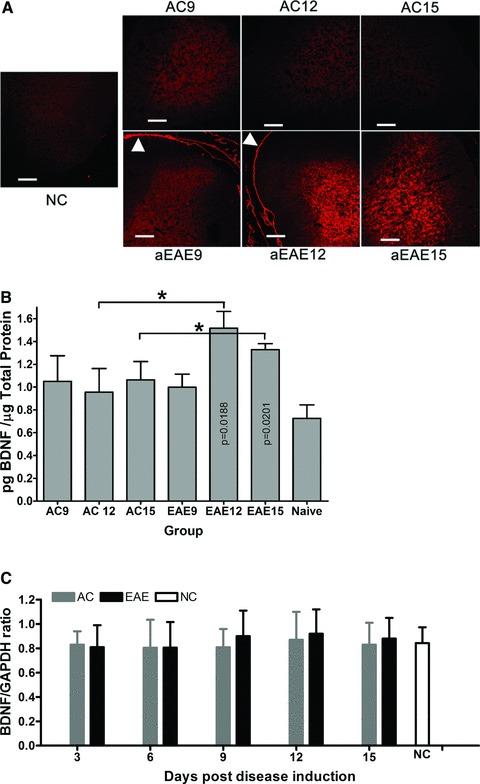
(A) BDNF immunoreactivity in spinal cord. Comparative IHC analysis of 10 μm sections of spinal cord showed markedly increased BDNF immunoreactivity at active EAE 12 dpi relative to active control. Active control spinal cord also shows increased BDNF immunoreactivity at 12 dpi, however, by 15 dpi, immunoreactivity is markedly reduced compared to active EAE spinal cord. Reticulocyte staining shows clearly in the dura of the active EAE spinal cord (arrow head). All images were taken at a total magnification of 100× and were exposed for 764 msec. with BDNF positive cells brightly labelled with red. Bar = 100 μm. (B) ELISA quantification of BDNF expression in the spinal cord. BDNF expression in the lumbar DRG was quantified using ELISA. Rats induced to a state of EAE show significantly increased BDNF expression compared to NC animals (*P < 0.05). Results are shown as pg/ml BDNF/μg total protein. (C) Real-time PCR results of BDNF expression within spinal cord. The BDNF mRNA expression of spinal cord for animals of the active EAE group (grey bars), at 12 dpi, is higher than other groups with an increasing trend (naïve control (white bar) and active control (black bars)) (*P > 0.05) with a one way ANOVA and Tukey’s post test based on two factors (day and group) using software SPSS 16.0.
